Canine Teeth in Humans: Functions, Evolution, and Importance
Canine teeth, also known as cuspids or “eye teeth,” hold a special place in our oral anatomy. These pointed teeth, with their characteristic shape and location, play crucial roles in our daily lives beyond just chewing. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of canine teeth in humans, exploring their functions, evolutionary history, and importance in our oral structure.
What Are Canine Teeth?
Canine teeth are pointed teeth located on either side of the incisors, usually one on each side of the upper and lower jaws. They are named “canine” due to their resemblance to the sharp, pointed teeth of dogs. Their unique shape sets them apart from other teeth in the human mouth.
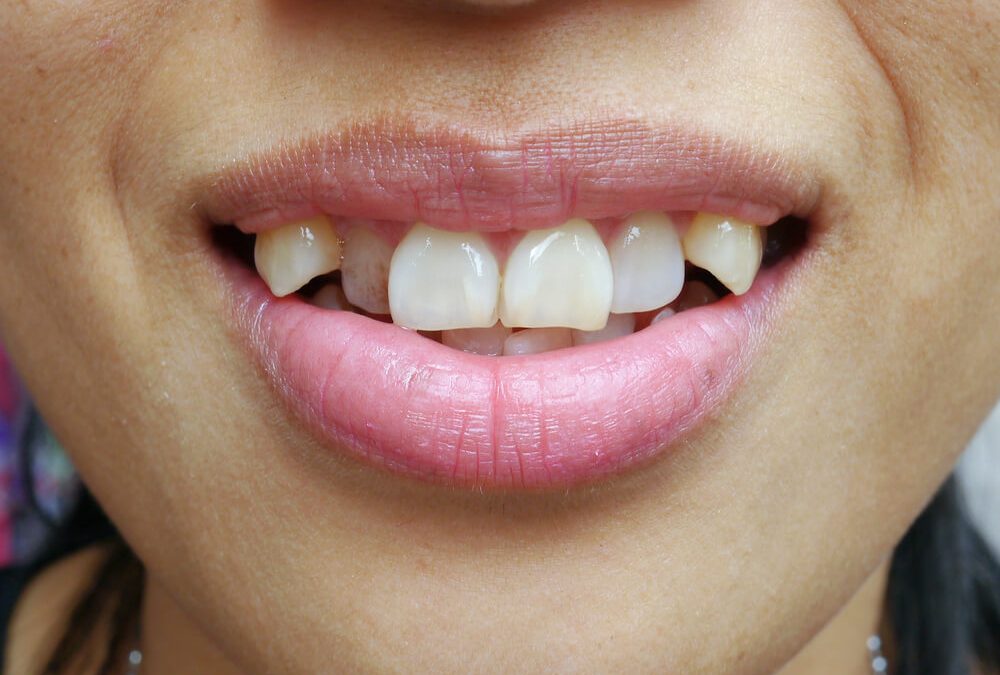
Canine teeth have a single, pointed cusp, designed to grip and tear food. This pointed shape is well-suited for their primary function: biting and tearing. Unlike molars, which have broad, flat surfaces for grinding, and incisors, which are flat and used for cutting, canine teeth are specialized for piercing and holding.
Functions of Canine Teeth
The functions of canine teeth extend far beyond the act of chewing. These teeth serve several crucial roles in our daily lives:
Efficient Biting:
Canine teeth are instrumental in biting into food. Their pointed shape allows for efficient penetration of various textures, making it easier to tear through tough or fibrous substances.
Speech and Pronunciation:
Canine teeth also play a significant role in our ability to articulate speech sounds. They are involved in producing certain consonant sounds, including the “th” sound in words like “this” and “that.”
Oral Health Support:
Canine teeth contribute to maintaining good oral health. They help guide the alignment of adjacent teeth and maintain the structural integrity of the dental arch.
Evolution of Canine Teeth in Humans
The story of canine teeth in humans is intertwined with our evolutionary journey. While modern humans may not rely on these teeth for survival as much as our distant ancestors did, their evolution provides valuable insights into our dietary adaptations and lifestyle changes.
The Early Role:
In our evolutionary past, our ancestors used canine teeth for hunting and tearing into the flesh of animals. These teeth were essential for survival, enabling them to access nutrient-rich animal protein.
Dietary Shifts:
As our diet evolved and diversified, the importance of canine teeth for hunting diminished. With the advent of cooking and food processing, we became better equipped to consume a wider range of foods.
Variations in Canine Teeth
While the fundamental anatomy of canine teeth remains consistent across humans, there are notable variations in these teeth among different populations and individuals. These variations can be influenced by genetics, geography, and cultural practices.
Cultural Significance:
In some cultures, canine teeth are considered symbols of strength or beauty. They may be intentionally modified or adorned as part of cultural traditions.
Genetic Factors:
Genetics plays a role in the size, shape, and positioning of canine teeth. These genetic variations contribute to the unique dental characteristics of different individuals.
Common Dental Issues Involving Canine Teeth
While canine teeth in humans serve essential functions, they are also susceptible to various dental issues. Understanding these issues and their symptoms can help individuals maintain their oral health.
Symptoms of Dental Issues:
Dental problems related to canine teeth may manifest as symptoms such as pain, sensitivity, swelling, or changes in tooth color. Individuals should pay attention to these signs and seek dental care when necessary.
Common Issues:
Discuss common dental issues involving canine teeth, including impaction, crowding, or abnormal growth patterns. Explain how these issues can affect oral health and quality of life.
The Significance of Canine Teeth in Anthropology
Canine teeth have played a role in the field of anthropology, contributing to our understanding of human history and evolution. Researchers have utilized canine teeth in various ways to glean insights into ancient human populations.
Identification of Remains:
Canine teeth, with their unique characteristics, have been used to identify human remains in archaeological discoveries. Their size, shape, and dental patterns can provide valuable information about ancient individuals.
Dietary Analysis:
By examining wear patterns and dental structure, anthropologists can infer the dietary habits of ancient populations. This information helps reconstruct the lifestyles and environments of our ancestors.
Caring for Your Canine Teeth
Taking proper care of your canine teeth is essential for overall oral health. Here are some tips for keeping your canine teeth and the rest of your smile in top condition:
Regular Dental Check-Ups:
Schedule routine dental check-ups with your dentist. These visits allow for the early detection of dental issues and preventive care.
Brushing and Flossing:
Practice good oral hygiene by brushing your teeth twice a day and flossing daily. Pay attention to your canine teeth, as they are susceptible to plaque and tartar buildup.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are canine teeth, and where are they located?
Canine teeth, also known as cuspids or “eye teeth,” are pointed teeth located on each side of the upper and lower jaws, typically one on each side.
2. What is the primary function of canine teeth in humans?
The primary function of canine teeth is to bite and tear food. Their pointed shape makes them efficient at piercing and holding, aiding in chewing and digestion.
3. Do canine teeth serve any other functions besides biting?
Yes, canine teeth also play a role in speech and pronunciation, contribute to maintaining oral health by guiding tooth alignment, and influence facial aesthetics.
4. How have canine teeth evolved in humans over time?
Canine teeth have evolved as our dietary habits changed. They were once crucial for hunting but have become less prominent as we adapted to diverse diets.
5. Are there variations in the size and shape of canine teeth among individuals?
Yes, genetic factors can lead to variations in the size and shape of canine teeth among individuals. These variations contribute to the uniqueness of dental features.
6. What are common dental issues involving canine teeth?
Common dental issues related to canine teeth include impaction, crowding, and abnormal growth patterns. These issues can affect oral health and require treatment.
7. Can canine teeth be used for identifying ancient human remains?
Yes, canine teeth, with their distinct characteristics, have been used by anthropologists to identify human remains in archaeological discoveries.
8. Are there any cultural practices related to canine teeth?
Yes, in some cultures, canine teeth are intentionally modified or adorned as part of cultural traditions, symbolizing strength or beauty.
9. How can I care for my canine teeth and maintain good oral health?
To care for your canine teeth, practice regular oral hygiene, including brushing, flossing, and using mouthwash. Schedule routine dental check-ups and maintain a balanced diet.
10. Can orthodontic treatments address issues related to canine teeth?
Yes, orthodontists can provide treatments to address issues such as misalignment or crowding of canine teeth, helping improve oral health and aesthetics.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, canine teeth in humans are not just ordinary teeth—they are remarkable in their structure, function, and significance. From their evolution as tools for survival to their role in speech, aesthetics, and our understanding of ancient societies, canine teeth have left an indelible mark on our species.




