The Threat of Super Gonorrhea What You Need to Know
Super Gonorrhea, a term that sounds like something out of a science fiction nightmare, has been making headlines in the world of sexual health. It represents a worrying development in the ongoing battle against the sexually transmitted infection (STI) known as gonorrhea. In this article, we will shed light on what super gonorrhea is, how it emerged, and why it’s causing concern in the medical community.
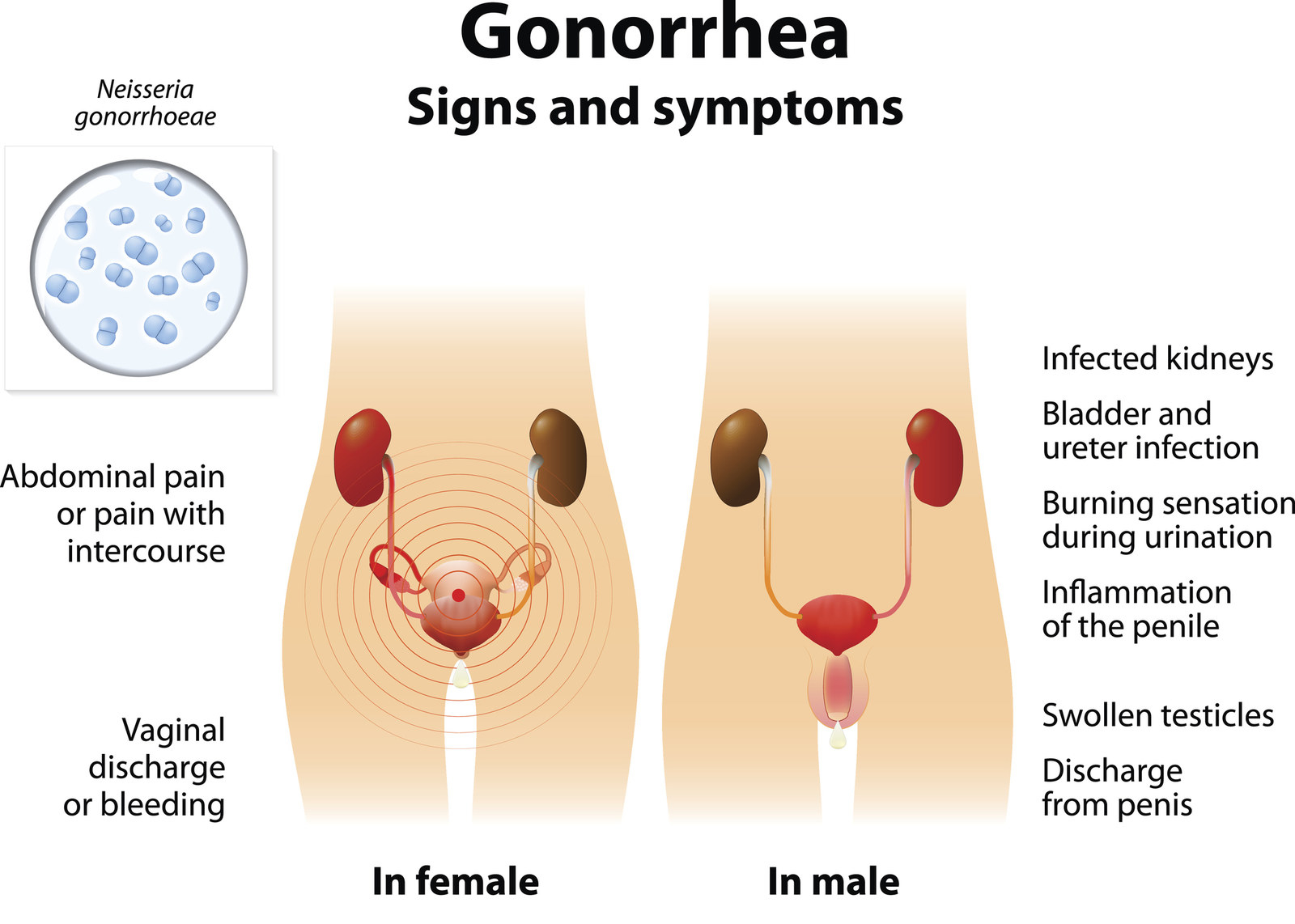
Understanding Gonorrhea Basics
What Is Gonorrhea and How Does It Spread?
Before delving into the intricacies of super gonorrhea, let’s get back to basics. Gonorrhea is a bacterial infection caused by Neisseria gonorrhoeae. It’s primarily transmitted through sexual contact—vaginal, anal, or oral. This bacterium thrives in warm and moist areas of the reproductive tract, but it can also affect the throat, rectum, and eyes.
Gonorrhea is a common STI that, in most cases, can be treated effectively with antibiotics. However, the emergence of antibiotic-resistant strains has given rise to the formidable super gonorrhea.
The Rise of Antibiotic-Resistant Gonorrhea
The Evolution of Super Gonorrhea
Super gonorrhea, also known as antibiotic-resistant gonorrhea, is essentially what its name suggests—an evolved and more resilient form of the gonorrhea bacterium. It has developed resistance to the antibiotics traditionally used to treat gonorrhea, such as ciprofloxacin, penicillin, and azithromycin.
Symptoms and Detection
Common Symptoms of Gonorrhea
Gonorrhea, including super gonorrhea, can manifest with a range of symptoms, although it’s worth noting that some individuals may be asymptomatic carriers. Typical symptoms include:
Painful Urination:
A burning sensation while urinating is a common symptom.
Unusual Discharge:
Men may experience white, yellow, or green discharge from the penis, while women may have increased vaginal discharge.
Pelvic Pain:
Women with gonorrhea may experience pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), leading to abdominal or pelvic pain.
Rectal and Throat Symptoms:
For individuals engaging in anal or oral sex, symptoms can include discomfort or discharge from the rectum or throat.
Diagnosing Super Gonorrhea: Challenges and Tests
Diagnosing super gonorrhea is crucial for effective treatment and prevention of its spread. However, it can be challenging due to the rise of asymptomatic carriers and the limitations of traditional testing methods. Healthcare providers typically use:
Nucleic Acid Amplification Tests (NAATs):
These highly sensitive tests detect the presence of gonorrhea DNA, making them the preferred method for diagnosis.
Urine Samples:
NAATs can be performed on urine samples, making testing more accessible.
Swab Samples:
In cases of symptomatic infections, swabs of the affected area (genital, rectal, or throat) are taken for testing.
Regular Screening:
Regular STI screenings, especially for individuals at higher risk, play a pivotal role in early detection.
Preventing Super Gonorrhea
Safe Practices and Barrier Methods
Preventing super gonorrhea and gonorrhea, in general, is crucial for public health. Here are some essential steps individuals can take:
Safe Sex:
Consistently and correctly using condoms during sexual intercourse can significantly reduce the risk of gonorrhea transmission.
Limiting Sexual Partners:
Reducing the number of sexual partners and practicing monogamy can lower the risk of exposure to gonorrhea.
Regular Screening:
Those at higher risk, including individuals with multiple partners or a history of STIs, should undergo regular screenings.
Treatment and Management
Current Treatment Approaches for Super Gonorrhea
Super gonorrhea’s resistance to common antibiotics complicates its treatment. Healthcare providers often rely on dual therapy, which combines two different antibiotics, such as ceftriaxone and azithromycin. However, the effectiveness of these treatments may vary based on regional antibiotic resistance patterns.
Emerging Treatments and Research
Researchers are actively exploring alternative treatments for super gonorrhea. These may include new antibiotics, phage therapy, and vaccines. Stay informed about ongoing research and consult healthcare providers for the latest treatment recommendations.
Public Health Implications
The Impact of Super Gonorrhea on Communities
Super gonorrhea poses significant challenges for public health. The potential for treatment-resistant strains to spread is a cause for concern. It’s crucial for healthcare systems and policymakers to prioritize strategies for monitoring, prevention, and treatment.
Surveillance:
Monitoring antibiotic resistance patterns and gonorrhea cases is essential.
Education:
Raising awareness about safe sexual practices and regular screening.
Research:
Supporting research into new treatments and prevention measures.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Super Gonorrhea
1. What is super gonorrhea, and how does it differ from regular gonorrhea?
Super gonorrhea is a form of gonorrhea that has become resistant to common antibiotics. Unlike regular gonorrhea, it cannot be easily treated with traditional medications.
2. How does super gonorrhea develop antibiotic resistance?
Super gonorrhea develops antibiotic resistance through genetic mutations that allow it to survive and thrive despite antibiotic treatment.
3. What are the symptoms of super gonorrhea?
Symptoms of super gonorrhea are similar to those of regular gonorrhea and can include painful urination, unusual discharge, and pelvic discomfort. However, super gonorrhea may be harder to treat.
4. Is super gonorrhea more contagious than regular gonorrhea?
Super gonorrhea is not necessarily more contagious, but it poses a greater challenge because it can be more difficult to treat, potentially leading to longer periods of infection.
5. How is super gonorrhea diagnosed?
Super gonorrhea is diagnosed through standard gonorrhea testing methods, such as nucleic acid amplification tests (NAATs). The difference lies in the antibiotic resistance profile revealed by the test.
6. Can super gonorrhea be cured?
While super gonorrhea can be more challenging to treat, it is not incurable. Healthcare providers typically use dual therapy, combining two different antibiotics, to address it.
7. What precautions can individuals take to avoid super gonorrhea?
Practicing safe sex, using condoms consistently and correctly, and getting regular STI screenings are essential precautions to avoid super gonorrhea.
8. Are there any vaccines or new treatments being developed for super gonorrhea?
Researchers are actively exploring new treatments, including phage therapy and vaccines, as potential solutions to combat super gonorrhea. However, these are still in development.
9. Is super gonorrhea a global health concern?
Yes, super gonorrhea is a global health concern due to its antibiotic resistance and potential for widespread transmission. It underscores the importance of responsible sexual health practices.
10. Where can I find more information and support for super gonorrhea?
Reliable sources like the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO) offer valuable information on super gonorrhea and sexual health.
Conclusion:
Super gonorrhea, with its antibiotic-resistant nature, presents a pressing threat to sexual health worldwide. The rise of treatment-resistant strains is a reminder that the battle against STIs is ongoing and ever-evolving. To combat super gonorrhea and reduce its impact, it’s crucial for individuals to prioritize responsible sexual health practices, including safe sex, regular screenings, and open communication with partners. Additionally, supporting ongoing research and public health initiatives is essential.




