The Trendelenburg Position Benefits and Uses
The Trendelenburg position, a staple in the realm of healthcare, holds a profound significance in patient care and medical procedures. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the origins, mechanics, and various applications of the Trendelenburg position, shedding light on its vital role in modern medicine.
History of the Trendelenburg Position
The Birth of a Medical Staple: A Historical Journey
Origins and Evolution:
The Trendelenburg position owes its name to the German surgeon Friedrich Trendelenburg, who introduced it in the 19th century. Initially used in surgery, this position has undergone significant refinements and adaptations over the years.
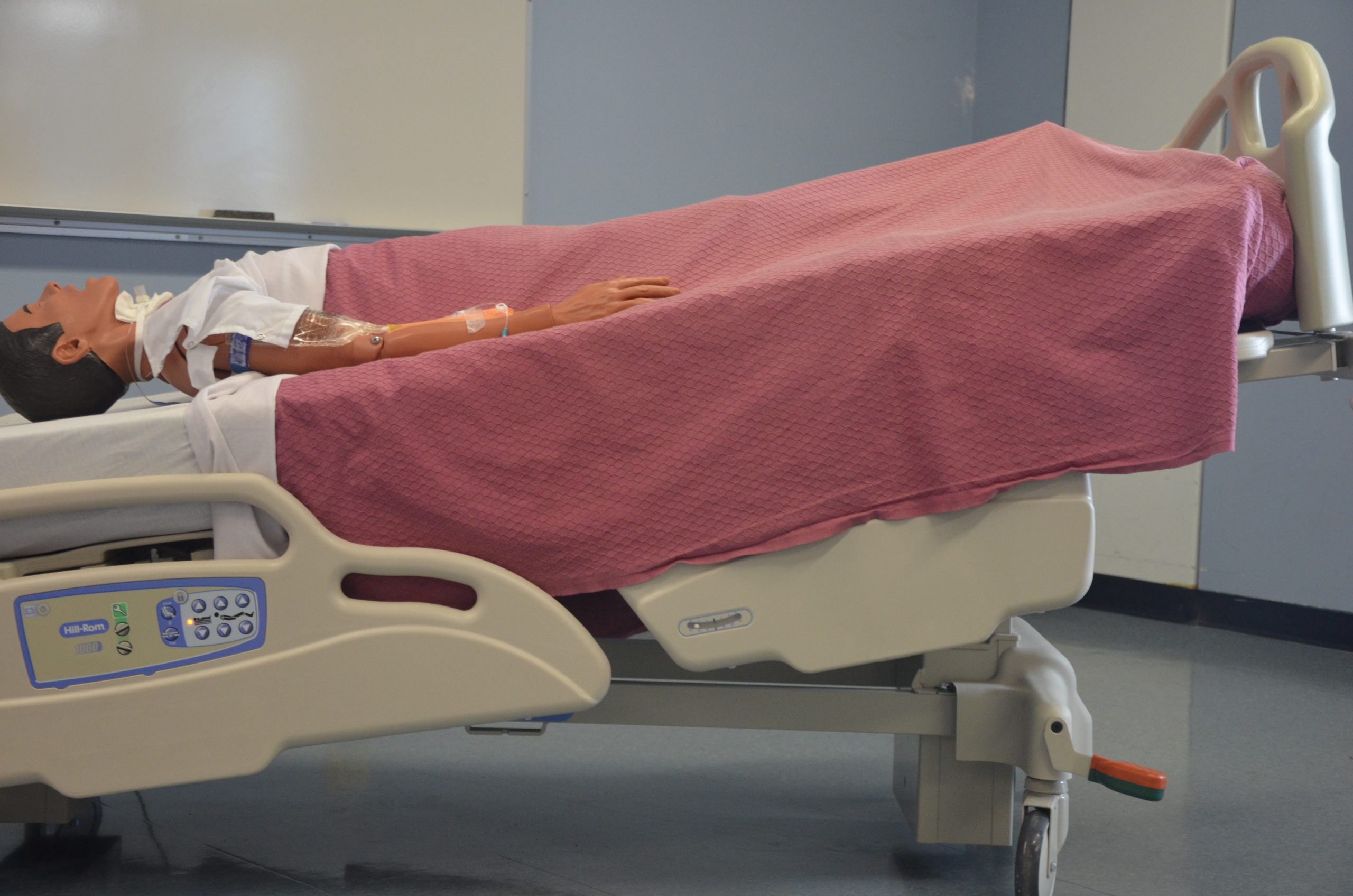
Adoption in Healthcare:
From its early days in surgery, the Trendelenburg position has found a place in a wide range of medical scenarios. Its history reflects not only medical progress but also the enduring value it brings to patient care.
Anatomy and Mechanics
Understanding the Position’s Impact on the Body
Anatomy at Play:
The Trendelenburg position involves tilting the body with the head lower than the feet. This simple yet effective change in body orientation has profound effects on circulation, respiration, and the cardiovascular system.
Blood Flow and Ventilation:
In this position, gravity assists in improving blood flow to vital organs and increases lung expansion. Understanding the anatomical changes is crucial to grasp why and when healthcare professionals employ them.
Medical Applications
Versatility in Medicine: Where the Trendelenburg Position Shines
Surgical Precision:
The Trendelenburg position is a staple in the world of surgery, especially in abdominal and pelvic procedures. Its inclination provides surgeons with improved access and visualization of the operative field.
Emergency Scenarios:
In emergency medicine, this position is often employed to manage hypotension and shock. Elevating the patient’s feet and legs can help improve blood flow to the brain and heart, stabilizing critical conditions.
Benefits and Risks
Balancing Act: Weighing the Pros and Cons
Advantages:
One of the primary benefits of the Trendelenburg position is its ability to enhance blood flow and oxygenation. It’s also valuable for reducing intraocular pressure during eye surgery and facilitating the drainage of bodily fluids.
Risks and Considerations:
While this position offers numerous advantages, it’s not without potential risks. These include potential complications related to blood pressure, lung function, and discomfort for patients in prolonged use.
Nursing Considerations
Guiding Hands: The Role of Nurses in Applying and Monitoring the Position
Implementing the Position:
Nurses play a vital role in placing patients in the Trendelenburg position and ensuring their comfort and safety. Proper assessment, positioning, and monitoring are key responsibilities.
Patient Safety:
Nurses must be attentive to patient comfort, potential complications, and the duration of Trendelenburg positioning. Clear communication with patients is essential to address their concerns and needs.
Patient Experience
Voices of Experience: Stories from Patients
Patient Perspectives:
To provide a well-rounded understanding, we’ve gathered stories and testimonials from individuals who have experienced the Trendelenburg position during medical procedures. Their insights shed light on the patient experience.
Diverse Experiences:
It’s important to remember that patients’ experiences can vary widely. While some may find the position discomforting, others may recognize its role in their recovery and overall well-being.
Research and Studies
Evolving Practices: Trends and Research Findings
Medical Advancements:
Ongoing research continues to refine the applications and benefits of the Trendelenburg position. We’ll explore recent studies and advancements in the use of this position in healthcare.
FAQ’S About trendelenburg
1. Q: What is the Trendelenburg position?
A: The Trendelenburg position is a medical posture where a patient’s head is lower than their feet. It’s often used to improve blood flow and access during surgical procedures.
2. Q: Why is the Trendelenburg position used in surgery?
A: This position allows surgeons better access to the abdominal and pelvic regions, enhancing visualization and facilitating certain procedures.
3. Q: Are there different variations of the Trendelenburg position?
A: Yes, there are variations like the Reverse Trendelenburg and the Modified Trendelenburg, each with specific applications in surgery and patient care.
4. Q: What are the medical benefits of the Trendelenburg position?
A: Benefits include improved blood flow to vital organs, reduced intraocular pressure during eye surgery, and enhanced drainage of bodily fluids.
5. Q: Can the Trendelenburg position help with low blood pressure and shock management?
A: Yes, elevating the feet and legs in the Trendelenburg position can improve blood flow to the brain and heart, aiding in managing low blood pressure and shock.
6. Q: Are there any risks associated with the Trendelenburg position?
A: While generally safe, prolonged use may have risks related to blood pressure, lung function, and patient discomfort, which should be monitored.
7. Q: What is the role of nurses in applying the Trendelenburg position?
A: Nurses play a crucial role in properly positioning patients, ensuring their comfort, and monitoring their condition while in the Trendelenburg position.
8. Q: How do patients typically experience the Trendelenburg position?
A: Patient experiences can vary, with some finding it uncomfortable and others recognizing its importance in their recovery.
9. Q: Are there ongoing research and advancements related to the Trendelenburg position?
A: Yes, ongoing research aims to refine its applications and explore new uses, contributing to improved patient care.
10. Q: Where can I find more information about the Trendelenburg position and its medical applications?
A: You can explore credible sources, medical journals, and research studies to gain in-depth insights into the Trendelenburg position and its role in healthcare.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Trendelenburg position stands as a testament to medical innovation and adaptability. From its historical roots to its modern-day applications, it remains a critical tool in enhancing patient care and surgical precision.




