The World of Cerebral Angiograms: A Closer Look at Brain Health
The health of our brain is undeniably crucial, as it governs everything from our thoughts and emotions to our body’s vital functions. When it comes to assessing the well-being of this vital organ, medical professionals often turn to a diagnostic tool known as a cerebral angiogram.
What is a Cerebral Angiogram?
Cerebral angiograms are medical procedures that provide a detailed view of the blood vessels in the brain. This diagnostic test is essential in identifying a wide range of neurological conditions, including aneurysms, blockages, and abnormal blood vessels.
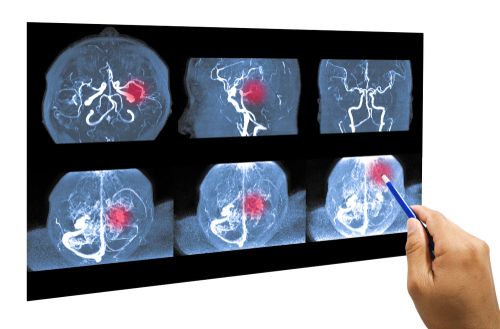
When and Why Doctors Recommend Cerebral Angiograms
Cerebral angiograms are typically recommended when a patient exhibits symptoms or risk factors associated with brain vascular issues. These symptoms may include severe headaches, vision problems, or neurological deficits. Doctors may also suggest this procedure if other non-invasive imaging tests are inconclusive.
The Procedure: How Cerebral Angiograms Are Performed
Understanding the intricacies of a cerebral angiogram can help alleviate any apprehensions you may have about the procedure. Here, we’ll walk you through the steps involved in this diagnostic test:
Preparation
Before the procedure begins, you’ll be prepared for the cerebral angiogram. This typically involves changing into a hospital gown and having an intravenous (IV) line inserted to administer medications and fluids as needed.
Local Anesthesia
To ensure your comfort, the medical team will administer a local anesthetic to numb the area where the catheter will be inserted. Usually, the catheter is introduced through a blood vessel in the groin or sometimes the wrist.
Catheter Insertion
A thin, flexible tube called a catheter is carefully guided through the blood vessels and directed toward the arteries in the brain. The catheter’s movement is monitored using advanced imaging technology, ensuring precise navigation.
Contrast Dye Injection
Once the catheter is in position, a contrast dye is injected through it. This dye is visible on X-ray images and helps highlight the blood vessels in the brain. X-ray images are continuously captured, providing real-time visualization.
Imaging and Diagnosis
As the contrast dye spreads through the brain’s blood vessels, X-ray images are captured from different angles. These images offer a comprehensive view of the brain’s vascular system, allowing doctors to identify any abnormalities or blockages.
Catheter Removal
After the necessary images have been obtained, the catheter is gently removed. Pressure may be applied to the insertion site to prevent bleeding, and a bandage is applied.
Recovery
Following the procedure, you’ll be monitored for a brief period in a recovery area. It’s common to experience some mild discomfort or grogginess, but this typically subsides quickly.
Indications for Cerebral Angiograms
Cerebral angiograms are a valuable tool for diagnosing a range of neurological conditions. Here, we’ll explore when doctors recommend this procedure and the symptoms or risk factors that warrant further investigation.
Identifying Specific Symptoms
Cerebral angiograms are often recommended when patients present with specific symptoms related to brain vascular issues. These symptoms can include:
Severe Headaches: If you experience sudden, severe headaches that are unusual for you, it may be a cause for concern.
Vision Problems: Changes in vision, such as blurriness or vision loss, may be indicative of underlying vascular issues in the brain.
Neurological Deficits: Any unexplained neurological deficits, such as weakness in limbs or difficulty speaking, should be assessed promptly.
Risk Factors and Pre-existing Conditions
In addition to symptoms, doctors may recommend cerebral angiograms for individuals with specific risk factors or pre-existing conditions, including:
Family History: A family history of aneurysms or other vascular disorders may increase your risk.
Hypertension: High blood pressure can contribute to vascular problems, making monitoring essential.
Previous Aneurysms: If you have previously experienced brain aneurysms, regular angiograms may be advised to monitor your condition.
Head Trauma: A history of head trauma can raise concerns about vascular injuries.
Suspected AVM: Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs), which are abnormal blood vessel connections, may require assessment.
FAQs about Cerebral Angiograms
Q: What is a cerebral angiogram, and why is it performed?
A: A cerebral angiogram is a diagnostic procedure that provides detailed images of blood vessels in the brain. It is performed to diagnose conditions like aneurysms, blockages, and vascular abnormalities.
Q: How is a cerebral angiogram different from other brain imaging tests?
A: Unlike non-invasive tests like MRI or CT scans, cerebral angiograms involve the insertion of a catheter to directly visualize blood vessels, offering superior detail.
Q: Are cerebral angiograms painful?
A: While you may feel some discomfort during the procedure, local anesthesia is used to minimize pain. Most patients tolerate it well.
Q: How long does a cerebral angiogram take?
A: The procedure typically lasts 1-2 hours, including preparation and recovery time.
Q: What are the risks associated with cerebral angiograms?
A: Potential risks include contrast dye allergies, bleeding, infection, and a small amount of radiation exposure.
Q: Can anyone undergo a cerebral angiogram, or are there specific criteria?
A: Cerebral angiograms are recommended based on symptoms, risk factors, or specific medical conditions. Your healthcare provider will determine if you need one.
Q: Is fasting required before a cerebral angiogram?
A: Yes, you’ll likely need to fast for several hours before the procedure. Your healthcare provider will provide specific instructions.
Q: How long is the recovery period after a cerebral angiogram?
A: Most patients can resume regular activities within a day or two, but it varies depending on individual factors.
Q: Are there alternatives to cerebral angiograms for diagnosing brain vascular conditions?
A: Yes, alternatives include CT angiography (CTA), magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), and transcranial Doppler (TCD) ultrasound.
Q: Can I discuss the risks and benefits of a cerebral angiogram with my healthcare provider?
A: Absolutely, it’s crucial to have a conversation with your healthcare provider to understand the procedure’s suitability and potential outcomes.
Conclusion:
In the intricate realm of brain health, the significance of diagnostic tools like cerebral angiograms cannot be overstated. These procedures serve as windows into the complex network of blood vessels that nourish our brains. From identifying aneurysms to pinpointing blockages, cerebral angiograms play a pivotal role in diagnosing neurological conditions that can impact our lives.




