Pulled Muscle in Chest: A Comprehensive Guide
A pulled muscle in the chest, although not as common as some other muscle injuries, can be incredibly discomforting and disruptive. Whether it’s due to a vigorous workout, an unexpected twist, or lifting something heavy, the pain can range from mild to severe. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into understanding chest muscle injuries, the anatomy behind them, and most importantly, how to effectively manage and recover from them.
Understanding Chest Muscle Injuries
Chest muscle injuries, often referred to as pulled or strained chest muscles, occur when the muscles in the chest are stretched or torn beyond their limits. These injuries can happen to anyone, from athletes to individuals engaged in everyday activities. Understanding the mechanics of these injuries and the importance of timely treatment is crucial for a quick recovery.
Importance of Timely Treatment
One of the critical aspects of dealing with a pulled muscle in the chest is seeking timely treatment. Neglecting the injury or not addressing it appropriately can lead to prolonged discomfort and potentially more severe complications. This guide will emphasize the significance of early intervention and provide insights into various treatment options available.
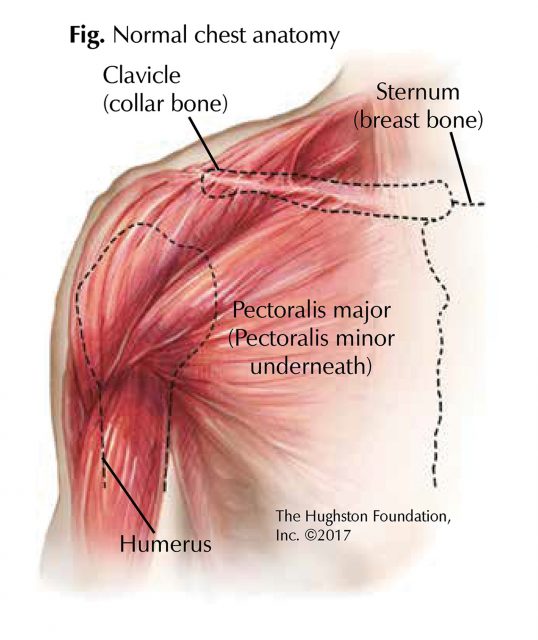
Anatomy of the Chest Muscles
A Closer Look at Chest Muscles
Before we dive into the causes and treatment of pulled chest muscles, let’s take a closer look at the chest muscles themselves. The chest is a complex area, housing several key muscle groups that play vital roles in upper body movement and stability. Understanding the anatomy of these muscles will help you grasp how injuries occur and why they can be painful.
How Chest Muscles Function
To comprehend chest muscle injuries better, it’s essential to know how these muscles function in daily activities. From lifting objects to simple tasks like reaching overhead, our chest muscles are involved in numerous movements. This section will provide insights into the role of chest muscles and why they are susceptible to injury.
Causes and Risk Factors
Common Triggers of Chest Muscle Injuries
Understanding what can lead to a pulled muscle in the chest is essential for prevention and early recognition. Some common triggers include:
Sudden Overexertion:
Activities that require sudden, forceful movements of the arms or torso can strain chest muscles.
Improper Lifting:
Lifting heavy objects without proper technique can put excessive strain on the chest muscles.
Sports Injuries:
Athletes, especially those involved in contact sports or activities with repetitive upper body motions, are at risk.
Accidental Falls:
Falling onto an outstretched arm or chest can result in muscle injuries.
Identifying Risk Factors
Certain factors can increase your susceptibility to chest muscle injuries. These include:
Lack of Warm-Up:
Failing to warm up before physical activity can make your muscles more vulnerable.
Muscle Imbalances:
Muscle imbalances, often caused by overtraining certain muscle groups, can lead to chest muscle strains.
Age:
As we age, our muscles may become less flexible, increasing the risk of injury.
Previous Injuries:
A history of chest muscle injuries can make you more prone to future occurrences.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing the Signs of a Pulled Chest Muscle
A pulled muscle in the chest typically manifests with various symptoms, including:
Pain:
The most prominent symptom is pain, which can range from a mild ache to sharp, intense discomfort.
Swelling:
Swelling or bruising may occur at the site of the injury.
Limited Range of Motion:
You might find it challenging to move your arm or torso without pain.
Muscle Spasms:
Muscle spasms or tightness in the chest area are common.
Diagnostic Procedures and Tests
To confirm a pulled chest muscle and rule out more severe injuries, your healthcare provider may recommend diagnostic procedures such as:
Physical Examination:
A thorough examination can help pinpoint the location and severity of the injury.
Imaging Tests:
X-rays or MRI scans may be ordered to visualize the extent of the muscle damage.
Electromyography (EMG):
In some cases, EMG may be used to assess muscle and nerve function.
Immediate Care and Home Remedies
First Aid for a Pulled Chest Muscle
When you suspect a pulled chest muscle, taking immediate action can make a significant difference in your recovery:
Rest:
Give your chest muscles time to heal by avoiding activities that worsen the pain.
Ice:
Apply ice to the injured area for 15-20 minutes every few hours during the initial 48 hours. This can help reduce inflammation.
Compression:
Gentle compression with an elastic bandage may provide support and minimize swelling.
Elevation:
Elevating your arm or chest may also help reduce swelling.
Home Remedies for Pain Relief
In addition to immediate care, several home remedies can alleviate discomfort during the recovery process:
Over-the-Counter Pain Relievers:
Non-prescription pain medications like ibuprofen can help manage pain and inflammation.
Heat Therapy:
After the initial 48 hours, applying heat with a warm compress or heating pad can relax tight muscles.
Gentle Stretching:
Gradual and controlled stretching exercises can prevent stiffness and improve flexibility.
Medical Treatment Options
Consultation with a Healthcare Professional
If your pulled chest muscle is severe or doesn’t improve with home care, seek medical attention. A healthcare provider will perform a thorough examination and recommend the most suitable treatment options. These may include:
Prescription Medications:
In some cases, stronger medications may be prescribed to manage pain and inflammation.
Physical Therapy:
A physical therapist can design a customized rehabilitation program to strengthen the chest muscles and improve range of motion.
Muscle Relaxants:
These medications can help relieve muscle spasms that often accompany pulled chest muscles.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Role of Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a pivotal role in the recovery process for a pulled chest muscle. Here’s how:
Targeted Exercises:
Physical therapists design exercises that specifically target the chest muscles, gradually restoring strength and flexibility.
Pain Management:
Therapists employ techniques to alleviate pain and discomfort, making it easier for you to participate in rehabilitation.
Prevention of Recurrence:
They provide guidance on proper form, body mechanics, and techniques to prevent future injuries.
Exercises and Rehabilitation Techniques
As you progress through rehabilitation, you can expect to perform various exercises, including:
Range of Motion Exercises:
These exercises focus on improving your chest’s flexibility and range of motion.
Strength Training:
Gradual strengthening exercises help rebuild chest muscle strength.
Stretching Routines:
Stretching exercises prevent muscle tightness and promote overall flexibility.
The Importance of Proper Warm-Up
Adequate warm-up is a crucial aspect of injury prevention. Engaging in light cardiovascular activities and dynamic stretching can prepare your chest muscles for more intensive workouts or physical tasks. Neglecting warm-up can increase the risk of muscle strains, not only in the chest but throughout the body.
FAQs: Pulled Chest Muscles
What causes a pulled chest muscle?
Pulled chest muscles are often caused by overstretching or tearing of the muscle fibers, usually due to sudden or excessive force.
Are there different types of chest muscle injuries?
Yes, chest muscle injuries can range from mild strains to more severe tears, each requiring varying levels of treatment.
How can I tell if I’ve pulled a chest muscle or if it’s something more serious?
While the symptoms of a pulled chest muscle are often sharp pain and limited range of motion, it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider for a proper diagnosis.
Can I continue exercising with a pulled chest muscle?
It’s generally recommended to rest and avoid strenuous activity until the muscle has healed to prevent further injury.
What’s the typical recovery time for a pulled chest muscle?
Recovery times vary depending on the severity of the injury, but most cases improve within a few weeks with proper care.
Is it necessary to see a doctor for a pulled chest muscle, or can I treat it at home?
While mild cases can often be managed at home with rest and home remedies, it’s advisable to consult a doctor, especially if the pain is severe or doesn’t improve.
Can a pulled chest muscle lead to complications if left untreated?
Yes, neglecting a pulled chest muscle can lead to complications like chronic pain, muscle weakness, or even muscle imbalances.
Are there specific exercises I can do to speed up the healing process?
Your healthcare provider or physical therapist can recommend specific exercises tailored to your injury and stage of recovery.
Can I prevent pulled chest muscles in the future?
Yes, adopting proper warm-up routines, maintaining good posture, and avoiding overexertion during exercises can reduce the risk of future injuries.
When is it safe to return to physical activities after a pulled chest muscle?
It’s safe to return to physical activities only when you have received clearance from a healthcare provider and your chest muscle has fully healed.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, dealing with a pulled muscle in the chest can be a challenging journey, but it’s one that can lead to a full recovery with the right approach. Let’s recap the key takeaways from this comprehensive guide: By empowering yourself with knowledge and taking proactive steps, you can effectively manage and recover from pulled chest muscles. Remember that every individual’s journey is unique, and it’s essential to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized guidance and treatment.




