Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia – Unraveling Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Management
ntroduction to Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia (IST)
In the intricate landscape of heart health, a condition known as Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia (IST) emerges as a complex phenomenon. IST, a type of cardiac arrhythmia, involves an accelerated heart rate that seems out of sync with the body’s demands. This article delves into the fundamental aspects of IST, from its definition to its implications on overall well-being.
Understanding the Basics of Cardiac Arrhythmias
Cardiac arrhythmias encompass a range of irregular heart rhythms that can disrupt the normal flow of blood and oxygen throughout the body. Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia, a specific form of arrhythmia, centers around a heart rate that exceeds the usual sinus rhythm, often during periods of rest. Unlike other arrhythmias caused by heart disease, IST primarily stems from dysfunction within the sinus node, the heart’s natural pacemaker.
Significance of Addressing IST for Heart Health
Given the critical role the heart plays in maintaining overall health, IST’s significance cannot be overstated. IST’s symptoms, if left unattended, can impact daily life, hinder physical activities, and lead to emotional distress. Early identification and management of IST can contribute to improved quality of life and potentially prevent complications down the road.
Symptoms of Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia
IST’s most recognizable signature is the rapid heartbeat that accompanies it. Individuals with IST often describe a sensation of their heart racing even when at rest. However, IST doesn’t stop at this hallmark symptom; it often reveals itself through a range of subtle yet impactful signs that shouldn’t be ignored.
Rapid Heartbeat: A Primary Indicator
A telltale sign of IST is a heart rate exceeding 100 beats per minute while at rest. This sensation of a racing heart might be accompanied by a fluttering sensation in the chest, further amplifying feelings of discomfort. Recognizing and addressing this primary indicator is crucial in determining the need for medical attention.
Unveiling the Subtle Signs: Palpitations, Dizziness, and Fatigue
Beyond the rapid heartbeat, IST can manifest through palpitations—irregular sensations of the heart’s beats. These palpitations might lead to a sense of unease and contribute to heightened anxiety. Additionally, dizziness and lightheadedness might surface due to the heart’s increased pace, affecting overall equilibrium. Fatigue, both physical and mental, can become prominent due to the strain IST places on the cardiovascular system.
Navigating Shortness of Breath and Chest Discomfort
IST’s effects extend beyond the heart itself, often causing shortness of breath even during mild physical activities. Individuals might find themselves gasping for air, struggling to catch their breath, or feeling as though their lungs can’t keep up with the heart’s rhythm. Furthermore, chest discomfort or mild pain might occur as the heart works harder to pump blood efficiently.
IST’s Impact on Quality of Life
The collective impact of IST’s symptoms can severely affect an individual’s quality of life. Everyday tasks that were once effortless may become daunting challenges. The psychological toll of living with an erratic heartbeat can lead to heightened stress levels and emotional strain. Recognizing the interconnectedness of these symptoms underscores the need for comprehensive management strategies.
Causes and Triggers of IST
Understanding the underlying factors that contribute to Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia is essential for devising effective management plans. While IST can emerge seemingly without a clear cause, several triggers and mechanisms have been identified that shed light on its origins.
Unraveling the Complexities: Factors Leading to IST
Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia often emerges in individuals without preexisting heart conditions. Instead, it appears to result from an intricate interplay of factors. Imbalances in the autonomic nervous system—the system responsible for regulating heart rate—can play a pivotal role. This dysregulation can cause the heart’s sinus node to fire rapidly and erratically, leading to the characteristic accelerated heartbeat of IST.
Role of Autonomic Nervous System Dysfunction
The autonomic nervous system consists of two branches: the sympathetic and parasympathetic. An overactive sympathetic branch and an underactive parasympathetic branch can disrupt the heart’s normal rhythm, contributing to IST. External stressors, anxiety, and hormonal imbalances can further exacerbate autonomic nervous system dysfunction, triggering episodes of rapid heartbeat.
Linking Hormonal Changes and IST Occurrence
Hormonal fluctuations, particularly among women, have been linked to the onset or exacerbation of IST. Changes in estrogen levels, such as those experienced during menstruation, pregnancy, or menopause, can impact the heart’s electrical activity and contribute to tachycardia. Understanding these hormonal influences is crucial, especially for individuals who notice a correlation between their cycle and IST episodes.
Potential Genetic Predisposition
While the exact genetic basis of IST remains a subject of ongoing research, there’s evidence to suggest a hereditary component. Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition that makes them more susceptible to autonomic nervous system imbalances or irregular heart rhythms. Exploring family medical history and genetic markers could offer insights into the likelihood of developing IST.
Diagnosis and Medical Evaluation
Accurate diagnosis of Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia is paramount to tailoring appropriate treatment plans. Medical professionals employ a combination of clinical evaluation, tests, and monitoring to confirm IST and rule out other potential cardiac issues.
Comprehensive Assessment: Clinical Examination and Patient History
During the diagnostic process, medical practitioners conduct thorough clinical assessments. They gather information about the patient’s medical history, including any existing heart conditions, lifestyle factors, and family history of heart ailments. This comprehensive understanding helps guide the diagnostic approach.
Electrocardiogram (ECG): Detecting IST Patterns
An Electrocardiogram, commonly known as an ECG or EKG, is a standard diagnostic tool used to record the heart’s electrical activity. When assessing IST, medical professionals closely analyze the ECG for patterns consistent with inappropriate sinus tachycardia. Peculiarities in the heart’s rhythm and rate can provide valuable insights.
Holter Monitoring: Capturing Transient Episodes
In cases where IST episodes are sporadic or transient, Holter monitoring becomes invaluable. This portable device continuously records the heart’s electrical activity over a 24-hour period or longer. By capturing data during various activities and situations, Holter monitoring aids in identifying irregular rhythms that might not be evident during a short clinic visit.
Stress Tests and Echocardiograms: Ruling Out Underlying Issues
To ensure accurate diagnosis, stress tests and echocardiograms are often conducted. Stress tests involve monitoring the heart’s response to physical exertion, helping assess how it functions under stress. Echocardiograms use sound waves to create images of the heart’s structure and function, allowing medical professionals to rule out any underlying structural issues that might mimic IST symptoms.
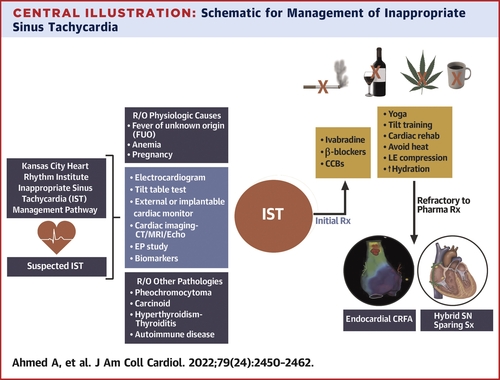
IST Treatment Approaches
Managing Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia requires a comprehensive approach that takes into account the individual’s symptoms, lifestyle, and overall health. Treatment strategies aim to alleviate symptoms, enhance quality of life, and reduce the frequency and intensity of IST episodes.
Lifestyle Modifications: Diet, Exercise, and Stress Management
Adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle can significantly impact the management of IST. Focus on a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. Regular exercise, tailored to individual capabilities, can help regulate heart function and reduce stress. Stress management techniques, such as meditation, deep breathing, and yoga, can aid in calming the autonomic nervous system and promoting overall well-being.
Medications: Beta-Blockers and Calcium Channel Blockers
Medications play a crucial role in managing IST, particularly in cases where lifestyle modifications alone may not suffice. Beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers are commonly prescribed. Beta-blockers slow down the heart rate and decrease its force of contraction, while calcium channel blockers relax the blood vessels and reduce the heart’s workload. These medications aim to bring the heart rate back to a more normal range.
inappropriate sinus tachycardia
Catheter Ablation: Targeted Intervention for Severe Cases
In cases where symptoms persist despite lifestyle changes and medication, catheter ablation may be considered. This minimally invasive procedure involves the insertion of a catheter into the heart to target and disrupt the abnormal electrical pathways causing IST. By ablating or disabling these pathways, the heart’s rhythm can be restored to a more regular pattern.
Exploring Emerging Therapies and Research Trends
Medical research continually evolves, and emerging therapies for IST are on the horizon. Researchers are investigating innovative approaches, such as neuromodulation techniques and targeted pharmaceutical interventions. Staying informed about these advancements can empower individuals and their healthcare providers to make informed decisions regarding treatment options.
Coping Strategies and Patient Support
Living with Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia can be emotionally challenging, but effective coping strategies can significantly enhance one’s well-being.
IST’s Psychological Impact: Anxiety and Stress Management
The psychological impact of IST extends beyond its physical symptoms. Anxiety and stress often accompany the condition, exacerbating symptoms and diminishing overall quality of life. Engaging in stress-reduction techniques, cognitive behavioral therapy, and seeking professional psychological support can help individuals manage these emotional challenges.
Connecting with Support Groups and Online Communities
Navigating IST can feel isolating, but connecting with others who share similar experiences can provide a sense of community and understanding. Joining support groups or participating in online forums allows individuals to exchange insights, coping strategies, and emotional support.
Educating Family and Friends for Enhanced Emotional Well-being
Raising awareness about IST among family and friends is essential for building a strong support network. Loved ones can provide crucial emotional support and understanding, helping individuals face the challenges of living with a chronic condition more effectively.
Expert Insights and Patient Stories
Gaining insights from medical experts and hearing the stories of individuals who have successfully managed IST can offer valuable perspectives.
Expert Interviews: Cardiologists and Electrophysiologists
Consulting with cardiologists and electrophysiologists—experts in heart rhythm disorders—can provide in-depth knowledge about IST and its management. These professionals can offer personalized guidance tailored to an individual’s specific situation.
Real-Life Experiences: How Patients Manage IST Effectively
Patient stories are a source of inspiration and practical advice. Learning from individuals who have successfully navigated the challenges of IST can offer hope and provide actionable strategies for symptom management.
Shared Tips and Encouragement for Those on a Similar Journey
The journey of managing IST is unique for each individual, but shared tips, encouragement, and resilience can be universal sources of strength. Knowing that others have overcome similar challenges can instill a sense of determination and optimism.
Prevention and Long-Term Management
While Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia may not always be preventable, adopting preventive measures and long-term management strategies can lead to better outcomes and improved quality of life.
FAQs About Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia
Q: What is Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia (IST)?
A: IST is a type of cardiac arrhythmia characterized by a heart rate that is faster than normal, often exceeding 100 beats per minute at rest.
Q: What causes Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia?
A: While the exact cause is complex, factors such as autonomic nervous system dysfunction, hormonal changes, and potential genetic predisposition can contribute to IST.
Q: What are the common symptoms of IST?
A: Rapid heartbeat, palpitations, dizziness, fatigue, shortness of breath, and chest discomfort are some common symptoms of IST.
Q: How is IST diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis involves clinical assessment, Electrocardiogram (ECG) analysis, Holter monitoring, stress tests, and echocardiograms to rule out other conditions.
Q: Can lifestyle modifications help manage IST?
A: Yes, adopting a heart-healthy diet, regular exercise, stress management techniques, and mindfulness practices can complement medical treatment for IST.
Q: What medications are used to treat IST?
A: Beta-blockers and calcium channel blockers are often prescribed to regulate heart rate and manage symptoms associated with IST.
Q: What is catheter ablation for IST?
A: Catheter ablation is a minimally invasive procedure that targets and disrupts abnormal electrical pathways causing IST, restoring a more regular heart rhythm.
Q: Is IST a hereditary condition?
A: While the genetic basis is still being studied, there’s evidence to suggest a potential genetic predisposition to IST in some individuals.
Q: How can stress impact IST?
A: Stress can exacerbate autonomic nervous system dysfunction, leading to increased heart rate and IST episodes. Stress management techniques are important.
Q: Can IST be completely cured?
A: While IST may not always be fully cured, effective management strategies can significantly reduce symptoms and improve overall quality of life.
Conclusion: Shaping a Heart-Healthy Future
In the intricate landscape of heart health, Inappropriate Sinus Tachycardia presents a unique challenge. By comprehending its causes, recognizing its symptoms, and embracing effective management strategies, individuals can reclaim control over their heart health and overall well-being.




