Venous Stasis Ulcer: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, and Prevention
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on venous stasis ulcers. In this article, we’ll delve into the world of venous stasis ulcers, understand what they are, recognize their symptoms, and explore effective treatment and prevention strategies. Venous stasis ulcers can be a challenging condition, but with the right knowledge and care, managing them becomes more achievable.
Understanding Venous Stasis Ulcers
What Are Venous Stasis Ulcers?
Venous stasis ulcers are open sores that typically develop on the lower legs. They are often associated with venous insufficiency, a condition where the veins in the legs have difficulty returning blood to the heart. As a result, blood pools in the lower legs, leading to increased pressure, skin changes, and ultimately, ulcer formation.
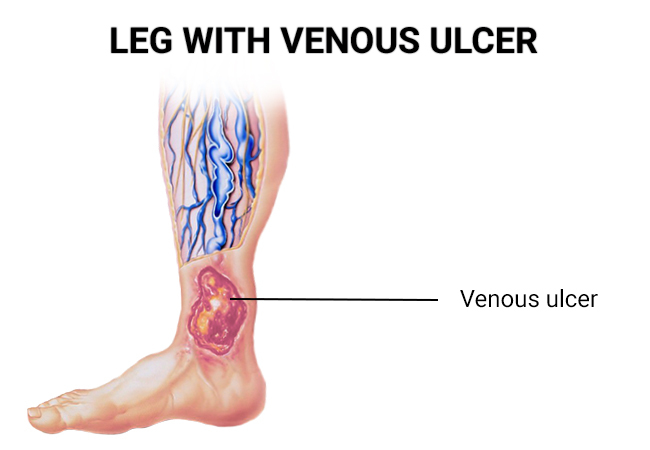
How Do Venous Stasis Ulcers Develop?
Venous stasis ulcers develop as a result of chronic venous insufficiency. When the veins struggle to push blood back up to the heart, it can lead to several key factors contributing to ulcer formation:
Increased Pressure:
Blood accumulates in the lower legs, causing elevated pressure in the veins.
Skin Changes:
Prolonged pressure and poor circulation can lead to skin changes, such as thickening and discoloration.
Tissue Damage:
Reduced blood flow deprives the tissues of oxygen and nutrients, leading to tissue damage and ulceration.
Symptoms of Venous Stasis Ulcers
Recognizing the Signs
Venous stasis ulcers often present with a set of distinctive symptoms, including:
Open Sores:
Ulcers appear as open, shallow wounds on the lower legs.
Pain:
Many individuals experience pain or discomfort in the affected area.
Swelling:
Swelling in the legs is a common symptom.
Skin Changes:
The skin surrounding the ulcer may become discolored, hardened, or scaly.
Diagnosing Venous Stasis Ulcers
Medical Evaluation
Diagnosing venous stasis ulcers typically begins with a thorough medical evaluation. A healthcare provider will:
Review Medical History:
Understanding your medical history, including any previous venous conditions or surgeries, is crucial.
Perform a Physical Examination:
A physical examination helps assess the condition of the ulcer and surrounding tissues.
Use Diagnostic Tools:
In some cases, diagnostic tests such as Doppler ultrasound may be used to evaluate blood flow in the affected veins.
Diagnostic Tests
Healthcare professionals may use various diagnostic tests to confirm the presence of venous stasis ulcers and assess their severity. These tests may include:
Doppler Ultrasound:
This non-invasive test assesses blood flow in the veins.
Photoplethysmography (PPG):
PPG measures changes in blood volume in the legs.
Venography:
A contrast dye is injected into a leg vein, and X-rays are taken to visualize blood flow.
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan.
Treating Venous Stasis Ulcers
Medical Treatment Options
The treatment of venous stasis ulcers often involves a combination of approaches:
Wound Care:
Proper wound care is essential to keep the ulcer clean and prevent infection.
Compression Therapy:
Compression stockings or bandages can help improve blood flow and reduce swelling.
Medications:
Healthcare providers may prescribe medications to manage pain or address underlying conditions.
Lifestyle Modifications:
Elevating the legs, regular exercise, and maintaining a healthy weight can aid in ulcer healing.
Lifestyle and Self-Care
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle modifications, and self-care practices play a significant role in managing venous stasis ulcers:
Compression Garments:
Wearing compression stockings or wraps as recommended by a healthcare provider.
Leg Elevation:
Elevating the legs above heart level when resting can reduce swelling.
Healthy Diet:
A balanced diet can support overall vascular health.
Exercise:
Engaging in regular, low-impact exercise can improve circulation.
Preventing Venous Stasis Ulcers
Reducing the Risk
Preventing venous stasis ulcers involves addressing the underlying causes and minimizing risk factors. Here are strategies to consider:
Venous Health Maintenance:
Maintain good venous health by staying active and avoiding prolonged sitting or standing.
Compression Therapy:
If you have a history of venous issues, consider compression stockings to support healthy blood flow.
Regular Checkups:
Routine checkups with a healthcare provider can help identify potential issues early.
Weight Management:
Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the strain on your veins.
Taking proactive steps can significantly reduce the risk of developing venous stasis ulcers.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are venous stasis ulcers, and how do they form?
Venous stasis ulcers are open sores that develop on the lower legs due to poor blood circulation caused by venous insufficiency. They form when tissue damage occurs due to blood pooling in the legs.
2. What are the common symptoms of venous stasis ulcers?
Typical symptoms include open sores on the legs, pain, swelling, and changes in the skin’s appearance, such as discoloration and hardening.
3. How are venous stasis ulcers diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a medical evaluation, and physical examination, and may include tests like Doppler ultrasound and venography to assess blood flow and confirm the condition.
4. What medical treatments are available for venous stasis ulcers?
Medical treatments may include wound care, compression therapy, medications, and lifestyle modifications to promote healing and alleviate symptoms.
5. Is venous stasis ulcer treatment painful?
Treatment discomfort varies from person to person, but healthcare providers take measures to minimize pain during wound care and compression therapy.
6. Can lifestyle changes help prevent venous stasis ulcers?
Yes, adopting a healthy lifestyle, maintaining a healthy weight, staying active, and using compression garments as recommended can reduce the risk of developing ulcers.
7. Are venous stasis ulcers a sign of a more serious underlying condition?
They often indicate an underlying issue, such as venous insufficiency, which should be addressed to prevent future ulcers.
8. Are there any complications associated with venous stasis ulcers?
Yes, complications can include infection, cellulitis, and delayed wound healing. Timely treatment is essential to prevent complications.
9. Can venous stasis ulcers heal on their own without treatment?
They are unlikely to heal without intervention. Medical treatment and self-care are essential for healing and preventing recurrence.
10. Can I continue normal activities while undergoing venous stasis ulcer treatment?
In most cases, individuals can continue with daily activities, but they should follow their healthcare provider’s recommendations for rest and exercise to support healing.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, venous stasis ulcers are a manageable condition with the right knowledge and care. By understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms, and adopting preventive measures, individuals can take control of their venous health and reduce the risk of ulcers.




