The human body is remarkably designed to heal itself. When you sustain a minor injury, your immune system typically kicks in, working to repair the damaged tissue efficiently. However, there are times when a wound may linger, refusing to heal despite appearing minor. Ignoring such a condition can result in serious complications. Understanding the causes, risks, and warning signs of non-healing wounds is crucial to ensure your health and well-being.
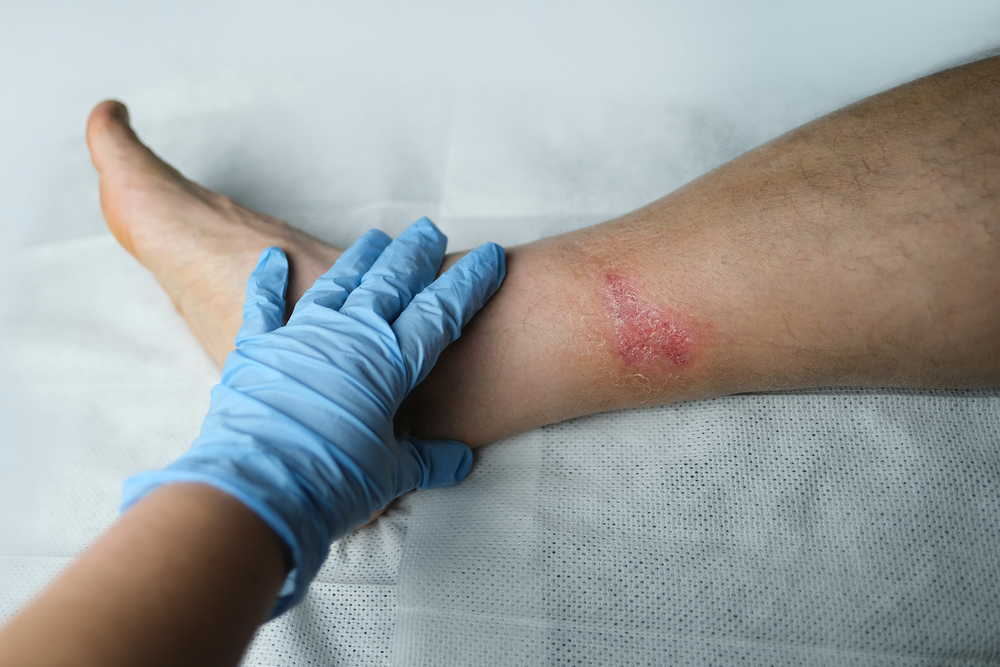
Why Do Some Wounds Fail to Heal?
There are several factors that may prevent a wound from healing properly. Identifying these issues early is essential for effective treatment.
1. Prolonged Healing Time
A typical minor wound should show significant improvement within two weeks. If your wound has persisted for over a month without noticeable progress, it requires medical evaluation. Delayed healing may indicate an underlying health issue that demands immediate attention.
2. Signs of Poor Healing
Tracking your wound’s healing progress is essential. Signs that your wound isn’t healing as it should include:
- Persistent redness or swelling
- Continuous drainage or pus formation
- A wound that scabs over but reopens repeatedly
- Skin that remains tender or painful around the wound site
If your wound seems to heal but frequently bleeds upon minimal contact, it could signal an abnormal recovery process that warrants medical consultation.
3. Recognizing Risk Factors
Certain medical conditions or lifestyle factors can increase your risk of developing non-healing wounds. Those most at risk include:
- Diabetics: High blood sugar levels can impair circulation, reducing the body’s ability to repair tissue.
- Smokers: Smoking restricts blood flow, slowing the healing process significantly.
- Chronic Steroid Users: These medications can suppress immune function, making wound recovery more challenging.
- Individuals Exposed to Radiation: Past radiation treatments may leave skin tissues damaged and less capable of healing.
4. Possible Underlying Causes
If your wound remains unhealed for weeks, there could be underlying medical concerns contributing to the problem. Potential causes include:
- Compromised Immune System: Conditions such as HIV, cancer, or autoimmune disorders may weaken your body’s ability to fight infection and repair tissues.
- Systemic Infections: A prolonged wound may be an indicator of a widespread infection affecting your body.
- Skin Cancer: In some cases, non-healing wounds may stem from skin cancer, particularly if they begin as warts or moles. Early detection through a biopsy can confirm this diagnosis.
Steps to Take if Your Wound Isn’t Healing
1. Clean and Dress the Wound Properly
Proper wound care is essential to promote healing. Clean the wound with mild soap and water, then apply a sterile dressing to protect it from dirt and bacteria.
2. Monitor the Wound Closely
Check your wound daily for signs of infection or worsening conditions. Record its size, color, and any drainage to provide accurate details when consulting with your doctor.
3. Seek Professional Medical Care
If your wound hasn’t improved within two weeks or shows signs of infection, it’s vital to visit a healthcare provider. Early intervention can prevent complications and improve treatment outcomes.
4. Undergo Diagnostic Testing
Your doctor may recommend diagnostic tests, such as:
- Blood tests to check for infections or underlying conditions
- Imaging tests to assess tissue damage
- Biopsies for suspected skin cancer cases
Treatment Options for Non-Healing Wounds
Effective treatment plans for chronic wounds often involve a combination of therapies. Common treatment approaches include:
1. Wound Debridement
This procedure involves removing dead or infected tissue to promote faster healing. Your doctor may use surgical, mechanical, or enzymatic methods for debridement.
2. Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT)
HBOT exposes your body to pure oxygen at high pressure, enhancing oxygen delivery to tissues and improving cell regeneration.
3. Antibiotics and Antimicrobial Treatments
If infection is the cause of delayed healing, antibiotics may be prescribed to manage bacterial growth.
4. Specialized Dressings and Topical Agents
Certain advanced dressings contain growth factors or collagen to accelerate tissue repair.
Prevention Tips for Non-Healing Wounds
Preventing non-healing wounds is essential, particularly for individuals at higher risk. Follow these tips to maintain healthy skin and minimize complications:
- Maintain proper hygiene and keep wounds clean
- Manage chronic conditions like diabetes with regular checkups
- Quit smoking to improve blood circulation
- Eat a balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals to support tissue repair
- Wear protective clothing when working in hazardous environments
FAQs
Q1: How long should a typical wound take to heal?
A minor wound should show noticeable healing within two weeks. If it persists beyond a month without improvement, consult your healthcare provider.
Q2: What are common signs that a wound isn’t healing properly?
Persistent redness, swelling, drainage, and recurring bleeding are key signs that your wound may not be healing as expected.
Q3: Can a non-healing wound be a sign of cancer?
Yes, some non-healing wounds may indicate skin cancer, particularly if they start as abnormal moles or warts. A biopsy can confirm this diagnosis.
Q4: Are diabetics at higher risk for non-healing wounds?
Yes, individuals with diabetes are prone to poor circulation, which can delay wound healing and increase infection risks.
Q5: What should I do if my wound bleeds repeatedly after healing?
Recurrent bleeding may suggest abnormal recovery or underlying conditions. Seek medical attention for proper assessment.




