Advancements in neurosurgical techniques have revolutionized how we treat complex brain conditions. Minimally invasive brain surgery now enables neurosurgeons to operate with precision while reducing trauma, minimizing incisions, and accelerating recovery. Patients today can undergo procedures with significantly less discomfort and complications, all while maintaining the surgical effectiveness required to address critical neurological issues.
Understanding Minimally Invasive Brain Surgery Techniques
What Is Minimally Invasive Brain Surgery?
Minimally invasive brain surgery refers to techniques that avoid large incisions and extensive manipulation of brain tissue. These procedures aim to preserve surrounding structures while still effectively treating conditions like tumors, epilepsy, or vascular abnormalities.
Key Techniques Used in Modern Neurosurgery
H3: Neuro-Navigation
Neuro-navigation functions like a GPS system for the brain. This computer-assisted technology uses imaging guidance to allow surgeons to locate brain tumors and other pathologies precisely. It reduces the need for large skull openings and ensures pinpoint accuracy.
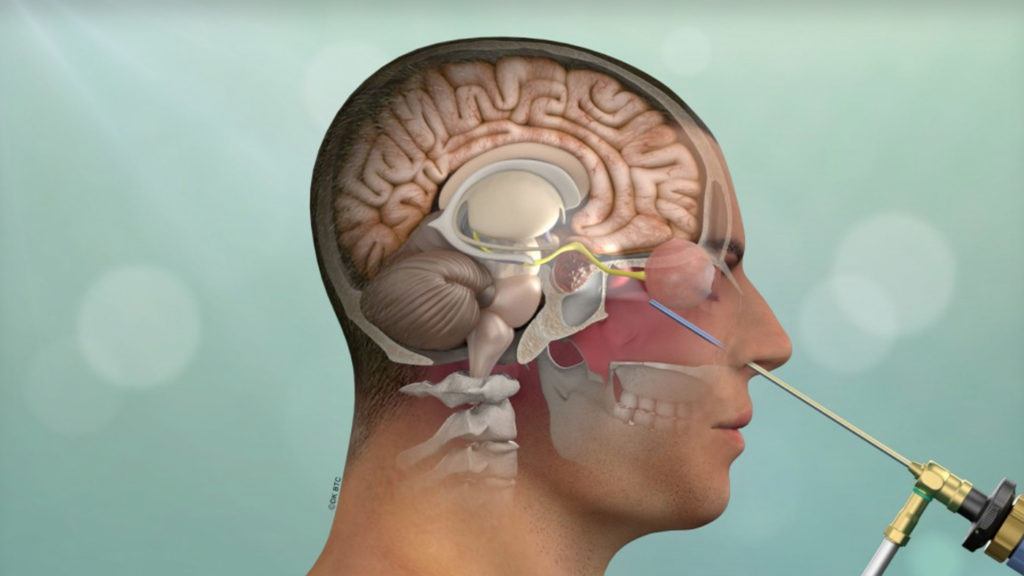
Endoscopic Brain Surgery
Using a small camera called an endoscope, surgeons make tiny incisions to access the brain. Real-time imaging allows them to operate without the need for full craniotomy, dramatically reducing recovery time and collateral tissue damage.
Keyhole Craniotomy
Also known as “keyhole surgery,” this method involves creating a small skull opening to perform intricate surgeries. It’s commonly used for tumor removal and aneurysm treatment, offering maximum results with minimum invasiveness.
Robotic-Assisted Neurosurgery
Robotic systems enhance surgical precision through computer-controlled instruments. Surgeons perform delicate maneuvers with exceptional control, minimizing damage to critical brain structures.
Laser Interstitial Thermal Therapy (LITT)
LITT uses a laser probe to thermally destroy abnormal tissue such as brain tumors. It is especially effective for deep-seated or inoperable lesions and involves minimal disruption of normal brain matter.
Benefits of Minimally Invasive Brain Surgery
Reduced Surgical Trauma and Scarring
Minimally invasive methods eliminate the need for large incisions, leading to less tissue trauma and fewer cosmetic concerns post-operation.
Accelerated Recovery and Shorter Hospital Stays
Patients undergoing minimally invasive surgery typically experience faster healing, reduced hospitalization, and a quicker return to daily activities.
Lower Infection and Complication Risks
Smaller wounds decrease the chance of infection, bleeding, and other complications associated with traditional brain surgeries.
Increased Surgical Accuracy
With advanced visualization tools and robotic assistance, minimally invasive surgery ensures optimal targeting of pathology while preserving healthy brain tissue.
Effectiveness of Minimally Invasive Neurosurgical Procedures
Numerous clinical studies confirm the efficacy of these methods in treating various neurological disorders:
-
Brain Tumors: Including meningiomas, gliomas, and metastases
-
Pituitary and Skull Base Tumors: Accessible through endoscopic transnasal approaches
-
Epilepsy and Movement Disorders: Treated through deep brain stimulation or lesionectomy
-
Vascular Lesions: Such as aneurysms and AVMs via keyhole or endovascular techniques
In many scenarios, minimally invasive procedures match or even exceed traditional surgical outcomes, particularly when paired with intraoperative imaging and navigation.
Candidate Selection for Minimally Invasive Brain Surgery
Who Can Benefit?
Ideal candidates often include individuals with:
-
Small to medium-sized brain tumors in accessible locations
-
Vascular abnormalities like aneurysms or AVMs
-
Focal epilepsy or movement disorders such as Parkinson’s disease
Patient eligibility is determined based on tumor location, patient age, overall health, and prior treatments.
The Future of Brain Surgery
Innovations in robotics, artificial intelligence, and augmented reality are pushing the boundaries of what is possible in neurosurgery. The trend toward smaller incisions and enhanced precision will likely redefine the standard of care.
As more procedures become feasible through minimally invasive approaches, patients can expect better outcomes, reduced risks, and improved quality of life post-surgery.
Frequently Asked Questions:
What conditions can be treated with minimally invasive brain surgery?
Brain tumors, pituitary tumors, aneurysms, epilepsy, and movement disorders are commonly treated using minimally invasive techniques.
Is the success rate comparable to traditional brain surgery?
Yes, in many cases, the outcomes are equal or superior due to increased surgical precision and reduced trauma.
Are these procedures available at all hospitals?
Advanced minimally invasive techniques are typically available at tertiary care or academic medical centers with specialized neurosurgical teams.
What are the risks involved?
Though lower than traditional methods, risks include bleeding, infection, or neurological deficits depending on the condition’s complexity.
Will insurance cover minimally invasive brain surgery?
Most insurance plans cover medically necessary brain surgeries, including minimally invasive options, but pre-authorization may be required.




