Understanding and Managing Radiation Burn
Radiation burn is a condition that arises due to exposure to various sources of radiation, which can lead to skin damage and discomfort. Whether through medical treatments, sunburn, or industrial accidents, understanding radiation burn is crucial for prevention and effective management. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the causes, symptoms, and steps you can take to deal with radiation burn.
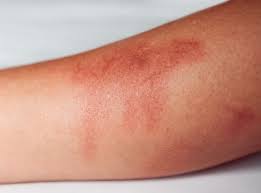
Causes and Risk Factors of Radiation Burn:
Radiation burn occurs when the skin is exposed to ionizing radiation, which damages skin cells and tissue. Medical procedures such as radiation therapy and X-rays, prolonged exposure to the sun’s ultraviolet rays, and accidents involving nuclear materials are common causes. Individuals undergoing radiation therapy, frequent X-rays, or working in radiation-prone environments are at a higher risk. It’s essential to recognize these risk factors to minimize the likelihood of radiation burn.
Common Symptoms of Radiation Burn:
Recognizing the symptoms of radiation burn is vital for early detection and appropriate action. The initial signs often include redness, similar to a sunburn, which may be accompanied by swelling and tenderness. As the condition progresses, the skin might develop blisters, become more painful, and even peel. In severe cases, radiation burn can cause open sores and lead to infection. Being aware of these symptoms empowers you to take timely steps toward managing radiation burn.
Types of Radiation Exposure Leading to Burns:
Radiation burn can result from various sources of radiation, each with its own characteristics and implications. Medical procedures involving radiation, such as cancer treatments and diagnostic imaging, are common sources. Sunburn, often caused by excessive sun exposure, can also lead to radiation burn. Additionally, accidents involving nuclear materials or industrial processes can expose individuals to high levels of radiation. Understanding these types of exposure helps you gauge the potential risks and take preventive measures accordingly.
Preventive Measures to Minimize Radiation Burn:
Prevention is key when it comes to radiation burn. To minimize the risk, consider wearing protective clothing that shields your skin from direct exposure to radiation sources. When outdoors, use sunscreen with a high sun protection factor (SPF) to reduce the impact of ultraviolet radiation. If you’re undergoing medical treatments involving radiation, discuss protective measures with your healthcare provider. By adopting these preventive strategies, you can significantly lower the chances of developing radiation burn.
First Aid and Immediate Care for Radiation Burn:
In cases of mild radiation burn, immediate action can aid in preventing further damage. Start by gently rinsing the affected area with cool water to remove any contaminants. Avoid using harsh soaps or scrubbing, as this can worsen the condition. Applying a cool, damp cloth can provide relief and soothe the skin. Refrain from using ice directly on the burn, as it can further damage the skin. Over-the-counter pain relievers and moisturizing creams can also offer comfort. For more severe cases, seek medical attention promptly to ensure proper care.
Medical Treatment and Professional Care:
For moderate to severe radiation burn cases, seeking medical attention is crucial. A healthcare professional can accurately assess the extent of the burn and recommend appropriate treatment. Depending on the severity, treatment may involve topical ointments, wound dressings, and pain management medications. In some cases, specialized wound care or antibiotics might be necessary to prevent infection. Regular follow-up appointments will ensure the burn is healing properly and any complications are addressed promptly.
Home Remedies and Self-Care:
While medical attention is vital, there are also steps you can take at home to aid in the healing process. Applying cool compresses or aloe vera gel to the affected area can provide relief from pain and inflammation. Keeping the area clean and dry, as well as avoiding tight clothing, can prevent friction and irritation. Hydration and a balanced diet rich in nutrients can support the body’s healing mechanisms. However, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional before attempting any home remedies to ensure they are appropriate for your specific situation.
Recovery and Follow-Up:
The recovery process for radiation burn varies depending on the severity of the burn and the individual’s overall health. Initially, the affected skin may peel or blister as new skin forms beneath. It’s crucial to avoid picking at or popping blisters, as this can increase the risk of infection. As the burn heals, it might change in appearance, and scars may develop. Regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider will allow for monitoring the progress and addressing any concerns that arise during the recovery phase.
FAQs About Radiation Burn
Q: What is radiation burn?
A: Radiation burn is a condition where skin damage occurs due to exposure to ionizing radiation, resulting in symptoms like redness, swelling, and blisters.
Q: What causes radiation burn?
A: Radiation burn can be caused by various sources, including medical procedures like radiation therapy, excessive sun exposure, and accidents involving nuclear materials.
Q: What are the symptoms of radiation burn?
A: Symptoms may include skin redness, tenderness, blistering, and peeling. Severe cases can lead to open sores and infection.
Q: Is radiation burn a common occurrence?
A: Radiation burn can occur in situations involving exposure to ionizing radiation, but its prevalence varies based on factors like the type and duration of exposure.
Q: How can I prevent radiation burn?
A: Preventive measures include wearing protective clothing, using high-SPF sunscreen, and following safety guidelines during medical treatments involving radiation.
Q: What should I do if I experience radiation burn?
A: For mild cases, rinse the area with cool water, apply a cool compress, and avoid harsh soaps. Seek medical attention for moderate to severe burns.
Q: Can radiation burn be treated at home?
A: Mild cases can benefit from home remedies like cool compresses and aloe vera gel. However, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for proper guidance.
Q: Are there long-term effects of radiation burn?
A: Depending on the severity, radiation burn can result in scarring and changes in skin texture. Regular follow-up appointments can help monitor recovery.
Q: What medical treatments are available for radiation burn?
A: Medical treatments may involve topical ointments, wound dressings, pain management, and specialized wound care if needed.
Q: Can radiation burn lead to complications?
A: Severe radiation burn can lead to infections, delayed wound healing, and potential long-term skin issues. Timely medical care minimizes such risks.
Conclusion
Understanding radiation burn, its causes, symptoms, and treatment options, empowers you to take proactive steps to prevent and manage this condition. By adopting preventive measures, seeking timely medical care, and practicing self-care, you can contribute to a smoother recovery and minimize the potential long-term effects of radiation burn. Remember that your well-being is a priority, and staying informed is key to ensuring optimal skin health and overall wellness.