Managing Pain Behind the Eye
Experiencing pain behind the eye is an unsettling and often debilitating sensation. It can be sharp, throbbing, or feel like pressure, making even the simplest tasks challenging. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the world of eye pain, exploring its various causes, symptoms, and effective management strategies.
What Does Pain Behind the Eye Feel Like?
When it comes to pain behind the eye, it’s crucial to understand the sensations it can encompass. This discomfort is not a one-size-fits-all experience; it can manifest in different ways:
Throbbing Pain:
Some individuals describe a pulsating or rhythmic ache behind the eye. This can be indicative of various underlying causes, including migraines.
Stabbing Sensation:
A sharp, stabbing pain behind the eye can be distressing. It may come and go suddenly or persist for longer periods.
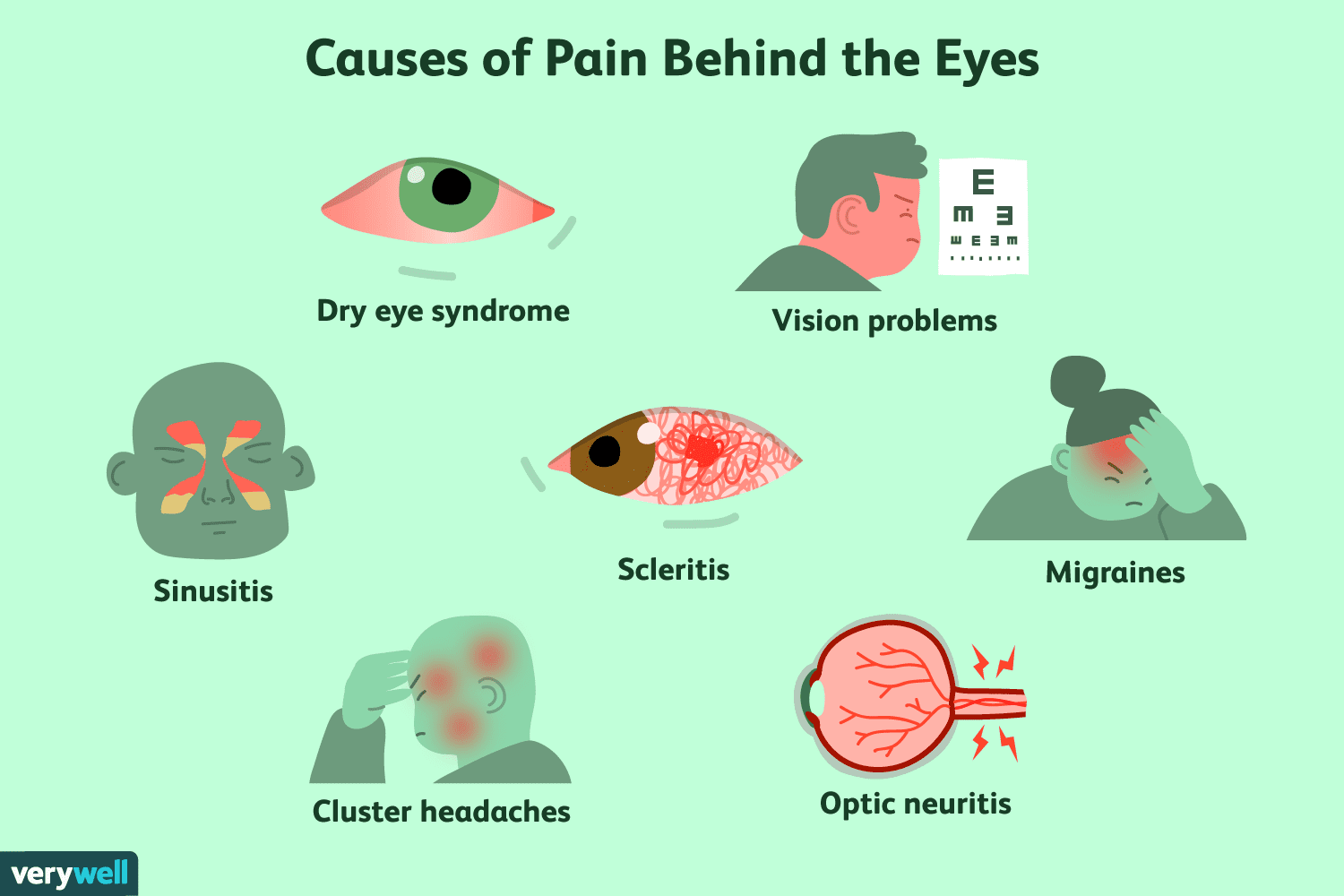
Common Causes of Pain Behind the Eye
Pain behind the eye can be triggered by a multitude of factors. To navigate this discomfort effectively, let’s explore some of the most prevalent causes:
Migraines:
Migraines often accompany severe throbbing pain behind one eye, along with other symptoms like nausea and sensitivity to light.
Sinusitis:
Inflammation or infection in the sinuses can lead to pressure and discomfort, radiating pain to the eyes and forehead.
Symptoms and Signs
Pain behind the eye often arrives with a host of additional symptoms and signs, providing valuable clues to its root cause. Recognizing these associated sensations can be pivotal in understanding your discomfort:
Blurred Vision:
Many individuals with eye pain also report blurred or distorted vision. This can range from mild blurriness to more pronounced visual disturbances.
Sensitivity to Light (Photophobia):
Pain behind the eye is frequently accompanied by an increased sensitivity to light. Even moderate light levels may become intolerable during episodes of eye pain.
When to Seek Medical Attention
While some instances of eye pain may resolve on their own or with simple home remedies, there are situations where seeking prompt medical attention is imperative. Pay close attention to the following warning signs:
Sudden, Severe Pain:
If you experience a sudden and excruciating pain behind the eye, especially if it’s accompanied by other concerning symptoms, such as loss of consciousness or severe nausea, seek emergency medical care immediately.
Persistent Pain:
If your eye pain persists for an extended period or worsens despite self-care measures, consult with a healthcare provider or an eye specialist.
Home Remedies and Self-Care
Managing mild to moderate pain behind the eye can often be achieved through self-care and home remedies. Here are some strategies that may provide relief:
Warm Compress:
Applying a warm compress to the affected eye can help relax the eye muscles and alleviate discomfort. Ensure the compress is not too hot and use it for 10-15 minutes at a time.
Rest Your Eyes:
If your eye pain is due to eye strain, take regular breaks from screens or close-up tasks. The 20-20-20 rule is helpful: every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for at least 20 seconds.
Medical Treatments
For more severe or persistent eye pain, medical treatments may be necessary. The approach will depend on the underlying cause:
Prescription Medications:
In cases of migraines or other specific conditions, a healthcare provider may prescribe medications to manage symptoms and prevent future episodes.
Antibiotics:
If your eye pain is linked to an infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to combat the underlying issue.
Prevention and Lifestyle Changes
Preventing recurrent episodes of eye pain involves making certain lifestyle adjustments:
Regular Eye Exams:
Schedule regular eye examinations to detect any underlying conditions early and ensure your prescription (if you wear glasses or contacts) is up-to-date.
Manage Allergies:
If you have allergies that affect your eyes, work with an allergist to manage your symptoms effectively.
Seeking Professional Help
While self-care measures and home remedies can be helpful, there are situations where professional assistance is essential:
Persistent or Worsening Symptoms:
If your eye pain persists or becomes more severe despite attempts at self-care, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare provider or an eye specialist. They can conduct a thorough evaluation to determine the underlying cause.
Chronic Conditions:
If you have a chronic eye condition like glaucoma or dry eye syndrome, regular follow-ups with an eye specialist are essential to monitor your condition and adjust your treatment plan as needed.
The Importance of Regular Eye Check-ups
Prevention is often the most effective way to maintain healthy eyes and prevent recurring eye pain. Regular eye check-ups are not just for those with pre-existing eye conditions; they are essential for everyone. Here’s why:
Early Detection:
Eye exams can detect potential issues early, allowing for timely treatment and preventing complications.
Prescription Updates:
If you wear glasses or contact lenses, regular check-ups ensure that your prescription is up-to-date, preventing eye strain and discomfort.
FAQs related to pain behind the eye
1. What causes pain in the eye?
Pain behind the eye can be caused by various factors, including migraines, sinusitis, eye strain, cluster headaches, or dry eye syndrome. Identifying the specific cause is crucial for effective treatment.
2. Is pain behind the eye a sign of a serious condition?
In some cases, yes. While eye pain can be benign and temporary, it can also indicate serious conditions such as glaucoma, tumors, or infections. If you’re concerned, consult a healthcare professional.
3. How can I relieve mild eye pain at home?
Home remedies include using a warm compress, resting your eyes, staying hydrated, practicing eye exercises, and over-the-counter pain relievers. However, the effectiveness may vary depending on the cause.
4. When should I seek immediate medical attention for eye pain?
You should seek immediate medical help if you experience sudden, severe eye pain, vision changes, or any signs of trauma or injury to the eye. These could be indications of serious issues.
5. Can allergies cause pain in the eye?
Yes, allergies can lead to eye discomfort, including pain behind the eye. Allergy medications and avoiding allergens can help alleviate symptoms.
6. What happens during a comprehensive eye exam?
A comprehensive eye exam assesses your visual acuity, checks for eye diseases, measures eye pressure, and evaluates the overall health of your eyes. It’s an essential part of preventive eye care.
7. Are there lifestyle changes to prevent recurring eye pain?
Yes, you can reduce the risk of recurring eye pain by managing screen time, staying hydrated, protecting your eyes during activities that pose injury risks, and maintaining a balanced diet.
8. What role do regular eye check-ups play in eye health?
Regular eye check-ups help detect eye conditions early, update prescriptions, and identify systemic health issues. They are vital for maintaining healthy eyes and preventing discomfort.
9. Can eye pain be a symptom of a migraine?
Yes, eye pain is a common symptom of migraines. It often presents as throbbing pain behind one eye, accompanied by other migraine symptoms.
10. Is eye pain always related to eye problems?
No, not always. While eye pain can originate from eye issues, it can also be linked to other health conditions. Consulting a healthcare provider can help determine the cause. Remember, if you have persistent or severe eye pain, consulting a healthcare professional is essential for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Conclusion
Pain behind the eye is not just an inconvenience; it can be a warning sign of underlying issues that require attention. Whether it’s managing mild discomfort at home or seeking professional help for chronic eye conditions, this guide has equipped you with the knowledge to make informed decisions about your eye health.




