Demystifying Arthrograms: What You Need to Know
Arthrograms are an essential tool in the realm of medical diagnostics, providing valuable insights into joint health and conditions. These specialized imaging procedures offer a unique window into the inner workings of our joints, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment of various orthopedic issues.
Why Arthrograms Matter in Medical Imaging
Arthrograms, often referred to as joint contrast studies, play a pivotal role in identifying problems within joints that may not be evident through other imaging techniques. They are particularly valuable in diagnosing conditions affecting the shoulders, knees, hips, and other joints.
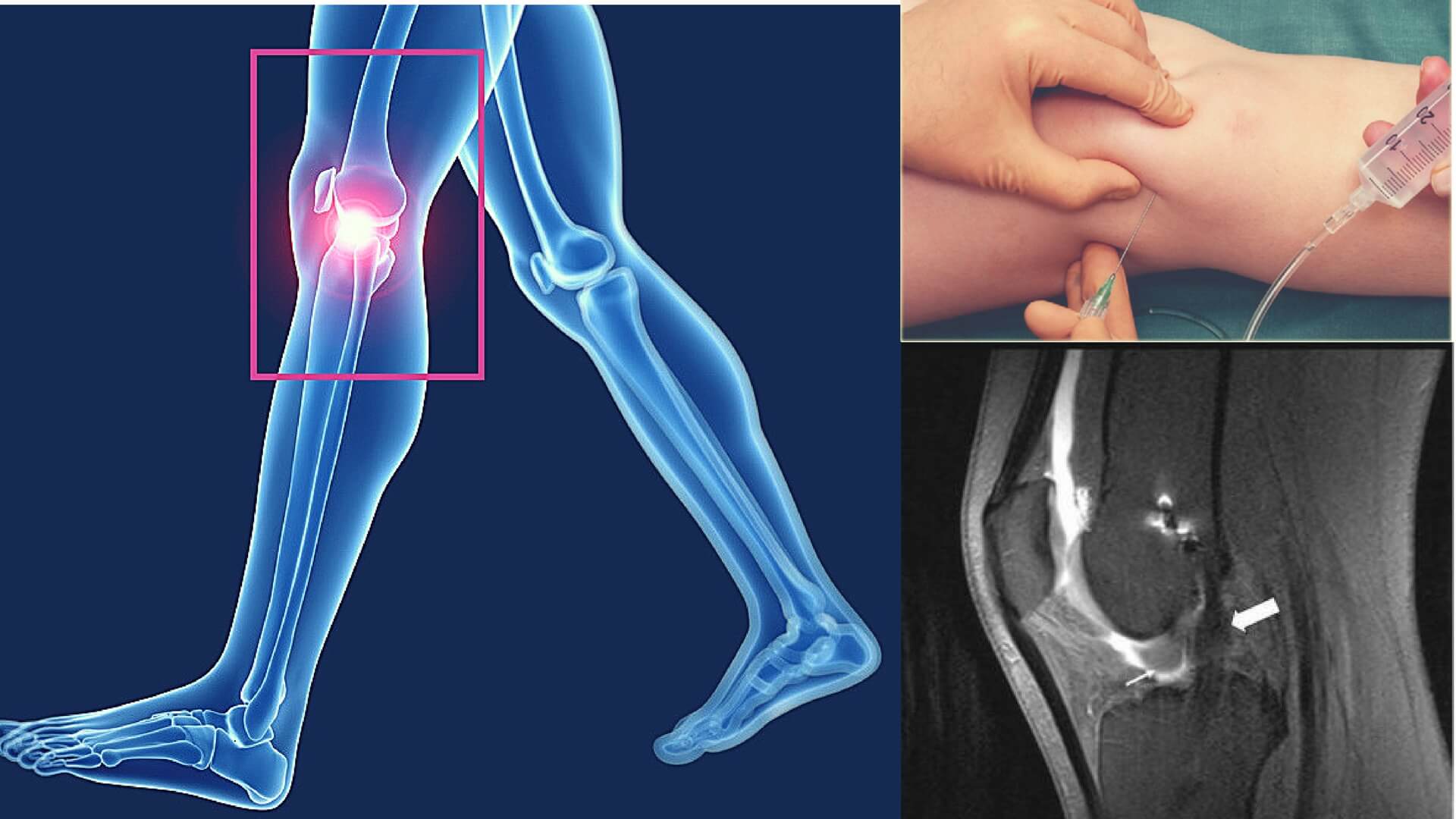
How Arthrograms Work
To comprehend the significance of arthrograms, it’s essential to understand how these procedures work. During an arthrogram, a contrast agent is injected directly into the joint being examined. This contrast material enhances visibility on X-rays, allowing for a detailed examination of the joint’s structure and function.
The Science Behind Arthrograms
The key to the effectiveness of arthrograms lies in the contrast agent used. Typically, iodine-based contrast agents are employed, as they provide excellent visibility under X-rays. Once injected into the joint, the contrast agent fills the joint space and coats the soft tissues within, creating a clear outline of the joint’s structures.
When Is an Arthrogram Needed?
The decision to undergo an arthrogram is typically based on a patient’s symptoms and medical history. These procedures are commonly recommended when there is suspicion of issues within a joint, such as:
Unexplained joint pain
Limited range of motion
Suspected ligament or tendon injuries
Evaluation of cartilage or labral tears
Detection of joint infections
Benefits of Arthrograms
Arthrograms offer several advantages in the realm of joint diagnostics and treatment planning. Here are some key benefits:
Enhanced Visualization
Arthrograms provide exceptionally clear and detailed images of the joint’s internal structures. The contrast dye injected into the joint enhances visibility on X-ray, MRI, or CT scans. This heightened clarity allows healthcare providers to identify and assess issues that may not be visible through other imaging methods.
Accurate Diagnosis
One of the primary purposes of an arthrogram is to diagnose various joint conditions accurately. This includes detecting ligament tears, cartilage damage, labral tears, and joint infections. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for developing an effective treatment plan tailored to the patient’s specific condition.
Minimally Invasive
Compared to surgical procedures like arthroscopy, arthrograms are minimally invasive. They require only a small injection into the joint, reducing the risk of complications and promoting quicker recovery times. Patients can typically resume their regular activities within a short period.
Guiding Treatment
Arthrograms not only aid in diagnosis but also serve as valuable tools for guiding treatment decisions. Once the underlying joint issue is identified, healthcare providers can determine the most appropriate course of action, whether it involves physical therapy, medication, or surgery.
Early Detection
Early detection of joint problems is critical for preventing the progression of conditions like osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis. Arthrograms can identify issues in their early stages, enabling prompt intervention and potentially preventing further joint damage.
Customized Care
Each patient’s joint condition is unique, and arthrograms allow for personalized treatment plans. By pinpointing the exact problem within the joint, healthcare providers can tailor treatments to address the specific needs and goals of the individual.
What to Expect During an Arthrogram
Understanding what happens during an arthrogram can help alleviate any anxiety patients may have before the procedure. Here’s a step-by-step overview of what typically occurs:
Preparation
Before the arthrogram, the patient may be asked to change into a hospital gown. In some cases, they may need to remove jewelry, accessories, or clothing that could interfere with the procedure. It’s essential to inform the healthcare team of any allergies, prior adverse reactions to contrast dye or pre-existing medical conditions.
Local Anesthesia
To ensure the procedure is as comfortable as possible, a local anesthetic is administered to numb the area around the joint. This minimizes any pain or discomfort during the injection of the contrast dye.
Injection of Contrast Dye
Once the anesthesia takes effect, the radiologist or healthcare provider will carefully insert a thin needle into the joint. This needle is used to inject the contrast dye directly into the joint space. Patients may feel a slight pressure or a sensation of fullness during this step.
Imaging
Immediately after the contrast dye injection, imaging studies like X-rays, MRIs, or CT scans are performed. These images capture the dye’s distribution within the joint, providing clear visuals of the joint’s internal structures. The patient may need to hold still or adjust their position during the imaging process.
Monitoring
Throughout the procedure, the healthcare team monitors the patient’s condition and ensures their comfort. Patients are encouraged to communicate any sensations or discomfort they may experience.
Post-Procedure Care
After the arthrogram, patients are typically observed for a brief period to ensure there are no immediate adverse reactions to the contrast dye. In most cases, patients can resume their normal activities, including driving, within a few hours. However, it’s advisable to have someone accompany them home after the procedure, especially if a sedative was administered.
Image Analysis
The collected images are carefully analyzed by a radiologist or orthopedic specialist. They interpret the images to make an accurate diagnosis and determine the most suitable treatment plan.
Potential Risks and Complications
Arthrograms are generally considered safe and well-tolerated. However, as with any medical procedure, there are potential risks and complications, although they are rare. Some possible issues include:
Infection at the injection site.
Allergic reactions to the contrast dye.
Bleeding or bruising around the joint.
Discomfort or pain during and after the procedure.
Patients are encouraged to discuss any concerns or questions they have with their healthcare provider before the arthrogram to ensure a safe and successful experience.
Recovery After an Arthrogram
Recovery after an arthrogram is generally straightforward, and most patients can resume their daily activities relatively quickly. Here’s what individuals can expect during the recovery period:
Immediate Post-Procedure Period
Immediately after the arthrogram, patients are usually monitored for a brief period to ensure there are no immediate complications or allergic reactions to the contrast dye. Some patients may experience mild discomfort, swelling, or bruising around the injection site, which is entirely normal.
Rest and Hydration
Patients should rest and stay well-hydrated on the day of the arthrogram. This can help the body flush out the contrast dye more effectively.
Pain Management
If there is any discomfort or pain after the procedure, over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be recommended by the healthcare provider. However, patients should follow their healthcare provider’s instructions regarding pain management carefully.
Returning to Normal Activities
In most cases, patients can return to their regular activities within a few hours after the arthrogram. Driving, working, and performing light activities should not be an issue. However, strenuous activities or heavy lifting should be avoided for a day or as advised by the healthcare provider.
Monitoring for Complications
Patients should keep an eye out for any signs of infection at the injection site, unusual swelling, severe pain, or an allergic reaction. If any of these symptoms occur, it’s crucial to contact their healthcare provider promptly.
Follow-Up Consultation
Patients will typically have a follow-up consultation with their healthcare provider or orthopedic specialist to discuss the results of the arthrogram. During this appointment, the images will be reviewed, and a diagnosis will be provided. Depending on the findings, a treatment plan may be recommended.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is an arthrogram, and how does it work?
An arthrogram is a medical imaging procedure that involves injecting contrast dye into a joint to enhance visibility on X-ray, MRI, or CT scans. It helps diagnose joint conditions by providing detailed images of the joint’s structures.
Is an arthrogram painful?
While the injection of contrast dye may cause temporary discomfort, it is generally not considered a painful procedure. Most patients find it tolerable.
How long does an arthrogram take?
The procedure itself typically takes around 30 minutes to an hour. However, you should plan for additional time for preparation and recovery.
Are there any risks associated with arthrograms?
Arthrograms are considered safe, but like any medical procedure, there are some risks, including infection, bleeding, or an allergic reaction to the contrast dye. These risks are rare and carefully managed.
Can I eat or drink before an arthrogram?
Your healthcare provider will provide specific instructions, but it’s common to fast for a few hours before the procedure, especially if sedation is involved.
How soon will I get the results of my arthrogram?
The time it takes to receive your results can vary, but typically, your healthcare provider will discuss the findings with you shortly after the images are analyzed.
What conditions can an arthrogram diagnose?
Arthrograms can diagnose a wide range of joint conditions, including ligament tears, cartilage damage, labral tears, and joint infections.
Are there any restrictions after an arthrogram?
Your provider may recommend limiting certain activities for a short time after the procedure. They will guide you when you can resume normal activities.
Is an arthrogram suitable for all joints?
Arthrograms can be used for many joints, but the suitability depends on your specific symptoms and the joint in question. Your healthcare provider will determine the most appropriate imaging method.
Is an arthrogram the same as an arthroscopy?
No, they are different procedures. An arthrogram is a diagnostic imaging test, while arthroscopy is a surgical procedure used for both the diagnosis and treatment of joint conditions.
Conclusion
In conclusion, an arthrogram is a valuable diagnostic tool that helps healthcare providers visualize the internal structures of joints with precision. While the procedure involves the injection of contrast dye and may cause mild discomfort, it is generally well-tolerated and safe.




