Demystifying PAC ECG: A Comprehensive Guide
In the world of cardiology and heart health, understanding the nuances of electrocardiograms (ECGs or EKGs) is crucial. One significant aspect that often raises questions is “PAC ECG” or “Premature Atrial Contractions” observed during these tests. This comprehensive guide aims to demystify PAC ECG, providing insights into what it entails, its significance, and how it impacts heart health.
What are Premature Atrial Contractions (PACs)?
Before delving into the intricacies of PAC ECG, let’s start with the basics: What exactly are Premature Atrial Contractions? In the context of your heart’s electrical system, PACs are irregular heartbeats that occur in the atria, the upper chambers of the heart. These contractions disrupt the normal rhythm, causing the atria to contract prematurely, often before the next regular heartbeat.
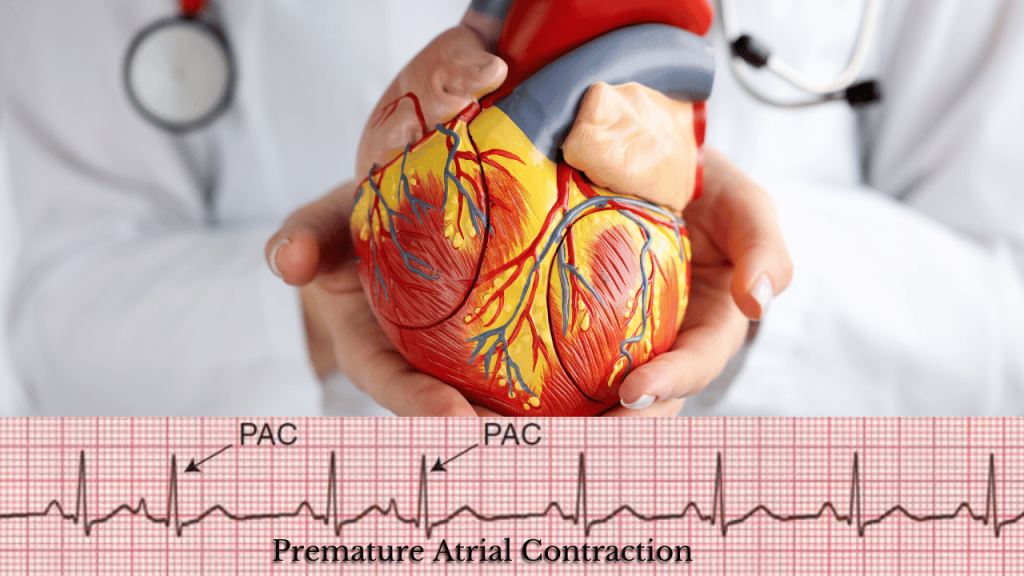
PACs can be visualized during an Electrocardiogram, a widely used diagnostic tool for assessing heart function. They manifest as abnormal spikes or irregularities in the ECG tracing. While PACs themselves may not always be a cause for concern, they can hint at underlying heart issues that need attention.
Symptoms and Signs of PAC ECG
Now that we have a foundational understanding of PACs, let’s explore how they manifest and what symptoms they may produce. PAC ECG irregularities often go unnoticed, but in some cases, individuals may experience:
Palpitations:
A sensation of fluttering or rapid heartbeat.
Occasional feelings of skipped beats or irregular rhythm.
Fluttering Sensations:
A feeling akin to butterflies in the chest.
A noticeable “thud” or “flip” in the heart’s rhythm.
Anxiety and Discomfort:
Some individuals may feel anxious or uncomfortable during PAC episodes.
Diagnosing PAC ECG
Diagnosing PAC ECG involves a collaborative effort between healthcare providers and the use of diagnostic tools like Electrocardiograms (ECGs or EKGs). Here’s how the process typically unfolds:
ECG Examination:
The first step is an ECG examination, a painless and non-invasive test.
During the ECG, electrodes are placed on specific areas of your chest, arms, and legs to record the heart’s electrical activity.
Any irregularities, including PACs, will be visible as deviations from the normal ECG pattern.
Interpretation by Healthcare Provider:
Once the ECG is complete, a trained healthcare provider, often a cardiologist or an electrophysiologist, interprets the results.
They will identify any abnormal rhythms, including PACs, and assess their significance.
Clinical Assessment:
If PACs are identified, the healthcare provider will conduct a clinical assessment.
This may involve discussing your medical history, lifestyle factors, and any symptoms you’ve experienced.
Rule Out Underlying Causes:
In some cases, additional tests may be needed to rule out underlying causes of PACs, such as heart disease or electrolyte imbalances.
These tests can include echocardiograms, blood tests, or Holter monitoring to record heart activity over an extended period.
Personalized Treatment Plan:
Based on the diagnosis and assessment, your healthcare provider will create a personalized treatment plan.
Treatment for PAC ECG may vary from person to person and can include lifestyle changes, medications, or further interventions.
It’s important to emphasize that not all PACs require treatment. In many cases, they are benign and do not pose a significant risk to heart health. However, if you are diagnosed with PACs, it’s crucial to follow your healthcare provider’s guidance for appropriate management.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the causes and risk factors of PACs is essential to addressing them effectively. PACs can occur due to various reasons, including:
Lifestyle Factors:
Excessive caffeine intake.
High levels of stress or anxiety.
Medical Conditions:
Underlying heart conditions, such as atrial fibrillation.
Electrolyte imbalances, particularly involving potassium and magnesium.
Medications and Stimulants:
Certain medications or stimulants affect the heart’s electrical system.
Aging:
PACs can become more common as individuals age, although they can occur at any age.
Treatment and Management of PAC ECG
The treatment and management of PAC ECG depend on various factors, including the frequency and severity of premature atrial contractions, underlying causes, and individual health considerations. Here’s an overview of potential approaches:
Lifestyle Modifications:
Reducing Caffeine Intake: If excessive caffeine consumption is a suspected cause, cutting back on caffeinated beverages like coffee and tea may help reduce PACs.
Stress Management: Stress-reduction techniques such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises can be beneficial.
Medications:
In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe medications to manage PAC ECG. These can include antiarrhythmic drugs or beta-blockers to regulate heart rhythm.
Medications are typically recommended when PACs are frequent, symptomatic, or associated with underlying heart conditions.
Addressing Underlying Causes:
If an underlying medical condition or electrolyte imbalance is contributing to PACs, addressing these issues is a crucial part of management.
Treatment may involve managing heart conditions, adjusting medications, or addressing specific electrolyte imbalances.
Lifestyle Choices:
Making heart-healthy lifestyle choices can play a significant role in managing PACs. This includes adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and avoiding excessive alcohol and tobacco use.
Regular Follow-Up:
For individuals diagnosed with PAC ECG, regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are essential.
These appointments allow for ongoing monitoring and adjustments to the treatment plan as needed.
Living with PAC ECG
Living with PAC ECG often involves adapting to a heart-healthy lifestyle and being mindful of potential triggers. Here are some tips for individuals managing PACs:
Stay Hydrated:
Proper hydration can help maintain electrolyte balance, reducing the risk of PACs.
Limit Stimulants: Minimize the consumption of stimulants like energy drinks and excessive caffeine.
Manage Stress:
Incorporate stress-reduction techniques into daily life to lower stress levels.
Stay Informed:
Keep informed about your condition and follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations.
Know When to Seek Help:
If you experience severe symptoms, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or fainting, seek immediate medical attention.
Prevention and Outlook
While PACs can be concerning, many individuals with benign PAC ECG can lead healthy lives with proper management. Preventive measures include:
Following a heart-healthy diet.
Staying physically active.
Managing stress effectively.
Reducing caffeine intake if necessary.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About PAC ECG
1. What are PACs in an ECG?
PACs, or Premature Atrial Contractions, are irregular heartbeats that occur in the atria, the upper chambers of the heart. They can be observed in an Electrocardiogram (ECG) as abnormal contractions before the next regular heartbeat.
2. Are PACs in ECG tests a cause for concern?
Not always. Isolated PACs are often benign and may not require treatment. However, frequent or symptomatic PACs should be evaluated by a healthcare provider.
3. What symptoms can PAC ECG irregularities produce?
Some individuals may experience palpitations, a fluttering sensation in the chest, or occasional skipped heartbeats. However, many people with PACs do not notice any symptoms.
4. How are PACs diagnosed through ECG?
ECGs record the heart’s electrical activity. PACs are identified as irregularities or deviations from the normal ECG pattern, typically during a routine ECG examination.
5. Can PACs be indicative of a serious heart condition?
In some cases, PACs may be associated with underlying heart conditions. Frequent PACs or those linked to other symptoms may require further evaluation to rule out serious issues.
6. What lifestyle changes can help manage PAC ECG?
Lifestyle modifications include reducing caffeine intake, managing stress through relaxation techniques, and staying well-hydrated. These changes can often reduce the frequency of PACs.
7. Are medications commonly prescribed for PAC ECG treatment?
Medications, such as antiarrhythmic drugs or beta-blockers, may be prescribed if PACs are frequent, symptomatic, or associated with underlying heart conditions.
8. Can PAC ECG irregularities be prevented?
Preventive measures include adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle, staying hydrated, and reducing stimulant consumption. However, PACs may still occur due to various factors.
9. Is PAC ECG a lifelong condition?
PACs do not necessarily persist throughout life. Many individuals experience intermittent PACs that may be resolved with lifestyle changes and proper management.
10. How important is regular follow-up for individuals with PAC ECG?
Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are essential for monitoring PACs, adjusting treatment plans if necessary, and ensuring overall heart health.
Conclusion
In our journey through the world of PAC ECG, we’ve unraveled the complexities of Premature Atrial Contractions and their impact on heart health. Understanding and managing PACs can significantly contribute to your overall well-being.




