Urine Squamous Epithelial Cells: What You Should Know
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on urine squamous epithelial cells. In this article, we will delve into the world of urine squamous epithelial cells, exploring their significance in urinary tract health and the potential implications of their presence.
What Are Urine Squamous Epithelial Cells?
When analyzing urine samples, healthcare professionals often encounter various cell types. One of these is the urine squamous epithelial cell. These cells are a type of epithelial cell, characterized by their flat, scale-like appearance when viewed under a microscope. But what exactly are urine squamous epithelial cells?
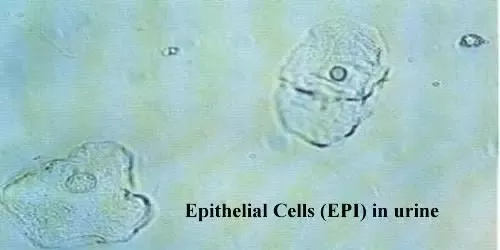
urine squamous epithelial cells
Understanding Urine Squamous Epithelial Cells:
Urine squamous epithelial cells are a specific type of epithelial cell lining found in the urinary tract. They serve as a protective barrier, lining the urethra, bladder, and parts of the renal pelvis. These cells play a crucial role in preventing harmful substances from entering the urinary system and help maintain the health of the urinary tract.
The Appearance of Urine Squamous Epithelial Cells:
When urine samples are examined under a microscope, these cells are easily recognizable due to their flat, irregular shape, similar to the scales of a fish or the tiles of a mosaic. This unique appearance distinguishes them from other cell types commonly found in urine.
Origin and Function:
Urine squamous epithelial cells originate from the lining of the urethra and other parts of the urinary tract. Their primary function is to provide a protective barrier that prevents toxins, bacteria, and other harmful substances from entering deeper into the urinary system. In essence, they act as the first line of defense in maintaining urinary tract health.
Significance of Urine Squamous Epithelial Cells:
Understanding the presence of urine squamous epithelial cells is significant for several reasons:
Diagnostic Value:
These cells can provide valuable diagnostic insights when detected in urine samples.
Abnormal levels or patterns of urine squamous epithelial cells may indicate an underlying urinary tract issue.
Symptoms and Health Implications:
Explore the potential symptoms and health implications associated with the presence of these cells.
Mention that further evaluation and testing may be necessary when abnormal findings occur.
When Are Urine Squamous Epithelial Cells Considered Normal?
It’s important to note that the presence of urine squamous epithelial cells can be considered normal under certain circumstances:
Routine Shedding:
Explain that a small number of these cells may be shed as part of the normal urinary tract shedding process.
Mention that isolated instances of squamous epithelial cells may not be a cause for concern.
Healthy Individuals:
Emphasize that healthy individuals can occasionally have these cells present in their urine without underlying issues.
Highlight that healthcare providers take into account the overall clinical picture when interpreting results.
Optimal Urinary Tract Health:
Stress that the presence of urine squamous epithelial cells alone does not necessarily indicate a problem.
Suggests that healthcare providers consider various factors, including symptoms and medical history.
Abnormal Findings and Potential Causes:
Understanding the potential causes of abnormal findings of urine squamous epithelial cells is crucial:
Identifying Abnormal Presence:
Explain how healthcare professionals identify an abnormal presence of squamous epithelial cells in urine.
Mention that abnormal findings may indicate an underlying urinary tract issue.
Potential Causes:
Explore various factors and conditions that can lead to elevated levels of urine squamous epithelial cells.
Highlight common causes, such as urinary tract infections, inflammation, or injury.
Symptoms and Health Conditions:
Discuss potential symptoms and health conditions associated with abnormal findings.
Emphasize the importance of seeking medical evaluation if symptoms persist or worsen.
Urinary Tract Health and Maintenance:
Maintaining optimal urinary tract health is essential:
Hydration and Diet:
Stress the importance of staying well-hydrated and maintaining a balanced diet.
Explain how adequate hydration can support overall urinary health.
Hygiene Practices:
Discuss the significance of good hygiene practices to prevent urinary tract issues.
Provide practical tips for maintaining cleanliness.
Regular Check-Ups:
Encourage readers to prioritize regular check-ups with healthcare providers.
Mention that early detection of urinary tract issues can lead to effective treatment.
Medical Evaluation and Tests:
In cases of persistent symptoms or abnormal findings, medical evaluation is necessary:
Consulting a Healthcare Provider:
Encourage readers to consult a healthcare provider if they have concerns about their urinary health.
Mention that healthcare professionals can determine the cause of symptoms and provide appropriate guidance.
Diagnostic Tests:
Explain the types of diagnostic tests that healthcare providers may recommend.
Mention urine analysis, imaging, and other relevant tests.
Treatment Options:
Briefly touch on potential treatment options based on the underlying cause of urinary tract issues.
Stress the importance of following a healthcare provider’s recommendations.
Prevention and Healthy Habits:
Preventing urinary tract issues and adopting healthy habits are key:
Dietary Choices:
Discuss the role of a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and hydration in maintaining urinary tract health.
Mention foods and beverages that can support urinary health.
Hydration Guidelines:
Provide guidelines on daily water intake for optimal hydration.
Explain how staying well-hydrated can help flush toxins from the urinary system.
Personal Hygiene:
Reiterate the importance of good personal hygiene practices.
Offer tips on maintaining cleanliness to reduce the risk of infection.
Lifestyle Adjustments:
Suggest lifestyle adjustments, such as avoiding smoking and managing stress.
Explain how these adjustments can positively impact urinary tract health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Urine Squamous Epithelial Cells
What are urine squamous epithelial cells?
Urine squamous epithelial cells are flat, scale-like cells found in the urinary tract lining, serving a protective role.
Are urine squamous epithelial cells normally present in urine samples?
Yes, a small number of these cells can be found in urine due to the natural shedding of the urinary tract lining.
When are urine squamous epithelial cells considered abnormal?
Elevated levels or unusual patterns of these cells may be considered abnormal and require further evaluation.
What can cause an abnormal presence of urine squamous epithelial cells?
Various factors, such as urinary tract infections, inflammation, or injury, can lead to abnormal findings.
Are there symptoms associated with an abnormal presence of these cells?
Abnormal findings may be associated with symptoms like urinary discomfort, frequent urination, or pain.
How can I maintain urinary tract health?
Staying well-hydrated, following good hygiene practices, and maintaining a balanced diet can support urinary tract health.
When should I seek medical evaluation for urinary tract issues?
consult a healthcare provider if you experience persistent symptoms or notice abnormal findings in urine samples.
What diagnostic tests can determine the cause of urinary tract issues?
Healthcare providers may recommend urine analysis, imaging, or other tests to diagnose the underlying cause.
What are the treatment options for urinary tract issues related to urine squamous epithelial cells?
Treatment options vary based on the underlying cause and may include antibiotics, lifestyle changes, or surgical interventions.
Is the presence of urine squamous epithelial cells a cause for immediate concern?
Not necessarily. Healthcare providers consider various factors, including symptoms and medical history, when interpreting results.
Conclusion
In this comprehensive guide, we’ve explored the world of urine squamous epithelial cells, their significance, and how they relate to urinary tract health. Armed with this knowledge, you’re better equipped to understand your body and take proactive steps towards a healthier you.




