Does HPV Go Away The Lifecycle of Human Papillomavirus
When it comes to Human Papillomavirus (HPV), questions often revolve around its lifecycle and whether it ever disappears from the body. In this comprehensive guide, we will dive deep into the world of HPV to understand its nature, progression, and the factors influencing its persistence. By the end, you’ll have a clear picture of whether HPV truly goes away and the implications it holds for your health.
Understanding HPV
Before we delve into the disappearance of HPV, let’s grasp the basics. HPV is a common virus transmitted through skin-to-skin contact, primarily during sexual activity. It encompasses over 200 different types, some of which can cause warts while others pose a more sinister threat by increasing the risk of cancer, particularly cervical cancer.
Understanding HPV’s prevalence is essential. It’s so common that nearly all sexually active individuals will encounter it at some point in their lives. This widespread presence necessitates a thorough exploration of its lifecycle and clearance from the body.
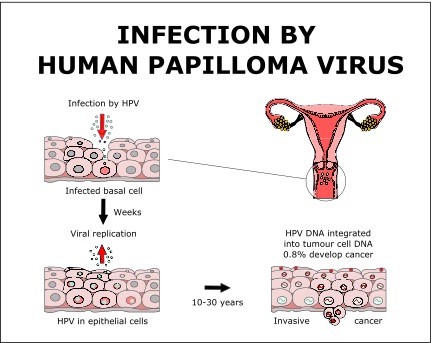
Natural History of HPV
Now, let’s uncover the natural history of HPV infections. Once exposed to the virus, individuals may wonder whether it simply disappears on its own or lingers indefinitely. HPV’s journey within the body can be complex and dynamic, influenced by various factors including the type of HPV, the individual’s immune response, and lifestyle choices.
In most cases, HPV infections are transient, meaning they go away without causing any symptoms or complications. This natural clearance typically occurs within two years of infection. However, it’s important to note that not all HPV infections follow this pattern. Some may persist for years, potentially increasing the risk of health issues, including cancer.
HPV Symptoms
In this section, we’ll explore the common symptoms associated with HPV infections. While some HPV infections are asymptomatic, others can manifest with noticeable signs. These symptoms may include genital warts, itching, or discomfort. By understanding the potential symptoms, you’ll be better equipped to recognize the presence of HPV and seek appropriate medical attention if needed.
Does HPV Go Away on Its Own?
Now, it’s time to address the pressing question: Does HPV go away without intervention? We’ll delve into the intricacies of HPV clearance and discuss factors that influence whether the virus is eliminated by the body’s immune system or persists over time. It’s important to provide readers with a clear understanding of the likelihood of HPV clearance and the variables that come into play.
Persistence of HPV
For those wondering why HPV may linger, this section will provide answers. We’ll explore the reasons behind persistent HPV infections and their potential implications. Highlighting the link between persistent HPV and an increased risk of cancer can underscore the importance of HPV awareness and proactive healthcare measures.
Diagnosing HPV
In this section, we’ll guide readers through the various methods and tests used to diagnose HPV. We’ll emphasize the importance of regular screenings and check-ups, which play a vital role in early detection and intervention. Keywords like “HPV diagnosis” and “HPV tests” will be naturally integrated to improve search engine visibility.
HPV Treatment Options
Now, let’s delve into the treatment options available for HPV. We’ll discuss medical and surgical interventions, focusing on managing symptoms and preventing complications. While keywords like “HPV treatment” and “HPV management” will be included, it’s essential to maintain a reader-centric approach, providing valuable insights for those seeking information on HPV management.
Reducing HPV Risk
Prevention is often the best strategy when it comes to HPV. In this section, we’ll provide practical tips and advice on reducing the risk of HPV infection. Emphasizing the importance of vaccination, safe sexual practices, and regular healthcare check-ups can not only optimize the content for SEO but also contribute to public health awareness.
Future Developments and Vaccination
This section will focus on current research and future developments related to HPV prevention and treatment. We’ll discuss ongoing vaccine advancements and their potential to reduce HPV-related health risks. Including keywords like “HPV vaccination” and “HPV prevention” will make the content more discoverable to those interested in staying updated on HPV-related developments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About HPV
1. What is HPV?
HPV, or Human Papillomavirus, is a common virus that is transmitted through skin-to-skin contact, primarily during sexual activity. There are over 200 different types of HPV, some of which can cause warts, while others can increase the risk of cancer.
2. How is HPV transmitted?
HPV is primarily transmitted through sexual contact, including vaginal, anal, and oral sex. It can also be spread through close skin-to-skin contact with an infected person.
3. Are there any symptoms of HPV?
Many HPV infections are asymptomatic, meaning they do not cause noticeable symptoms. However, some types of HPV can cause genital warts, while others may lead to cancer. Regular screenings are crucial for early detection.
4. Does HPV go away on its own?
In many cases, HPV infections clear on their own within two years. However, some infections may persist, potentially increasing the risk of health issues, including cancer.
5. Can HPV be cured?
There is no specific cure for HPV, but the immune system can often clear the infection. Medical treatments are available for managing symptoms and preventing complications.
6. How is HPV diagnosed?
HPV can be diagnosed through various methods, including Pap tests and HPV DNA tests. Regular screenings and check-ups are essential for early detection.
7. What are the risk factors for persistent HPV?
Factors such as a weakened immune system, smoking, and certain high-risk HPV types can increase the likelihood of persistent HPV infections.
8. Is there an HPV vaccine?
Yes, there are HPV vaccines available that can protect against some of the most common and high-risk types of HPV. Vaccination is a key preventive measure.
9. How can I reduce my risk of HPV?
Reducing your risk of HPV includes practicing safe sex, getting vaccinated, and attending regular check-ups and screenings. These measures are essential for prevention.
10. What should I do if I have HPV?
If you are diagnosed with HPV, it’s important to follow your healthcare provider’s recommendations. Depending on the type and severity of the infection, they may suggest monitoring, treatment for symptoms, or further evaluation.
Conclusion:
In the concluding section, we’ll summarize the key takeaways from the article. Reiterate the main points about HPV, its lifecycle, and the importance of prevention and regular check-ups. Ensure that the conclusion is concise and provides a clear answer to the question, “Does HPV go away?” This section also provides an opportunity to reinforce relevant keywords.




