Intramuscular Injection: A Comprehensive Guide
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on intramuscular injection. In this article, we will delve into the details of this medical procedure, providing you with all the necessary information you need to know. Intramuscular injection is a common method used to administer medications into the muscle tissue for rapid absorption and effectiveness.
Understanding Intramuscular Injection
Intramuscular injection, also known as IM injection, is a technique that involves injecting medications directly into the muscle tissue. This method allows for the efficient absorption of medications into the bloodstream, leading to a quicker onset of action compared to other routes of administration.
When is Intramuscular Injection Used?
Intramuscular injection is commonly used in various medical settings, including hospitals, clinics, and even at home. It is often preferred when medications need to be quickly absorbed and have a prolonged effect. Some common situations where intramuscular injection is used include:
Administering vaccines
Delivering antibiotics
Providing pain relief medications
Administering hormonal treatments
The Intramuscular Injection Process
The intramuscular injection process involves several key steps to ensure safety and efficacy:
Preparation: Gather all the necessary equipment, including the medication, syringe, needle, alcohol swabs, and a sharps container for safe disposal.
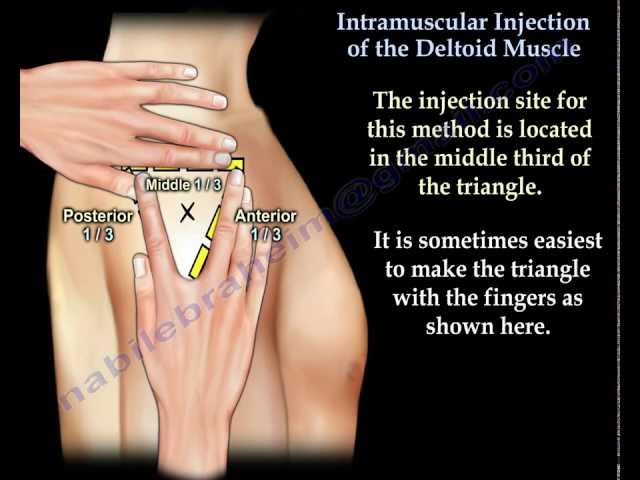
Site Selection: Identify the appropriate injection site. Common sites for intramuscular injections include the deltoid muscle in the upper arm, the gluteus maximus in the buttocks, and the vastus lateralis in the thigh.
Cleanliness: Cleanse the injection site with an alcohol swab to minimize the risk of infection.
Needle Insertion: Hold the syringe like a pencil and swiftly insert the needle into the muscle tissue at a 90-degree angle.
Aspiration: Pull back slightly on the plunger to check for blood return. If blood appears, withdraw the needle and choose a new injection site.
Medication Administration: Slowly inject the medication into the muscle tissue. The rate of injection should be controlled to avoid discomfort.
Needle Removal: Once the medication is administered, swiftly remove the needle from the injection site.
Disposal: Safely dispose of the used needle and syringe in a sharps container to prevent accidental injuries.
Post-Injection Care: Apply gentle pressure to the injection site using a sterile cotton ball or swab. If necessary, cover the site with a bandage.
Benefits and Considerations
Intramuscular injection offers several benefits, including:
The rapid absorption of medications
Prolonged effect of medications
Ability to administer larger volumes of medication
Reduced risk of medication degradation
However, there are some considerations to keep in mind:
Proper injection technique is crucial to ensure safety and efficacy.
Some medications may cause discomfort or pain at the injection site.
Injection sites should be rotated to prevent tissue damage or scarring.
Intramuscular injection is a widely used method for administering medications directly into the muscle tissue. It offers rapid absorption and prolonged effects, making it an effective route for various medications. By following proper injection techniques and considering the necessary precautions, intramuscular injections can be safely and effectively performed.
Frequently Asked Questions about Intramuscular Injection
1. What is an intramuscular injection?
An intramuscular injection is a method of administering medication directly into the muscle tissue using a syringe and needle.
2. Why are intramuscular injections used?
Intramuscular injections are used when certain medications need to be absorbed quickly or when the medication cannot be taken orally.
3. What are the common sites for intramuscular injections?
The common sites for intramuscular injections include the deltoid muscle in the upper arm, the vastus lateralis muscle in the thigh, and the gluteus maximus muscle in the buttocks.
4. How is an intramuscular injection administered?
An intramuscular injection is administered by inserting the needle into the muscle at a 90-degree angle and slowly injecting the medication.
5. Does an intramuscular injection hurt?
Some people may experience mild discomfort or pain during an intramuscular injection, but it is usually brief and tolerable.
6. What are the potential side effects of intramuscular injections?
Potential side effects of intramuscular injections may include pain at the injection site, bleeding, bruising, or infection. Rarely, allergic reactions or nerve damage may occur.
7. How long does it take for the medication to take effect after an intramuscular injection?
The time it takes for the medication to take effect can vary depending on the specific medication and individual factors. Generally, it may take a few minutes to a couple of hours.
8. Can anyone administer an intramuscular injection?
Intramuscular injections are typically administered by healthcare professionals such as doctors, nurses, or trained medical personnel.
9. Are there any special precautions to take before getting an intramuscular injection?
Before getting an intramuscular injection, it is important to inform your healthcare provider about any allergies, medical conditions, or medications you are currently taking. They will assess if any precautions need to be taken.
10. Can intramuscular injections be self-administered?
In some cases, individuals may be trained to self-administer intramuscular injections under the guidance of their healthcare provider. However, this should only be done after proper instruction and guidance.




