Arthritis in Thumb: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Management
Arthritis in the thumb can impact daily life. Discover the causes, signs, and proven strategies to manage discomfort and regain thumb mobility.
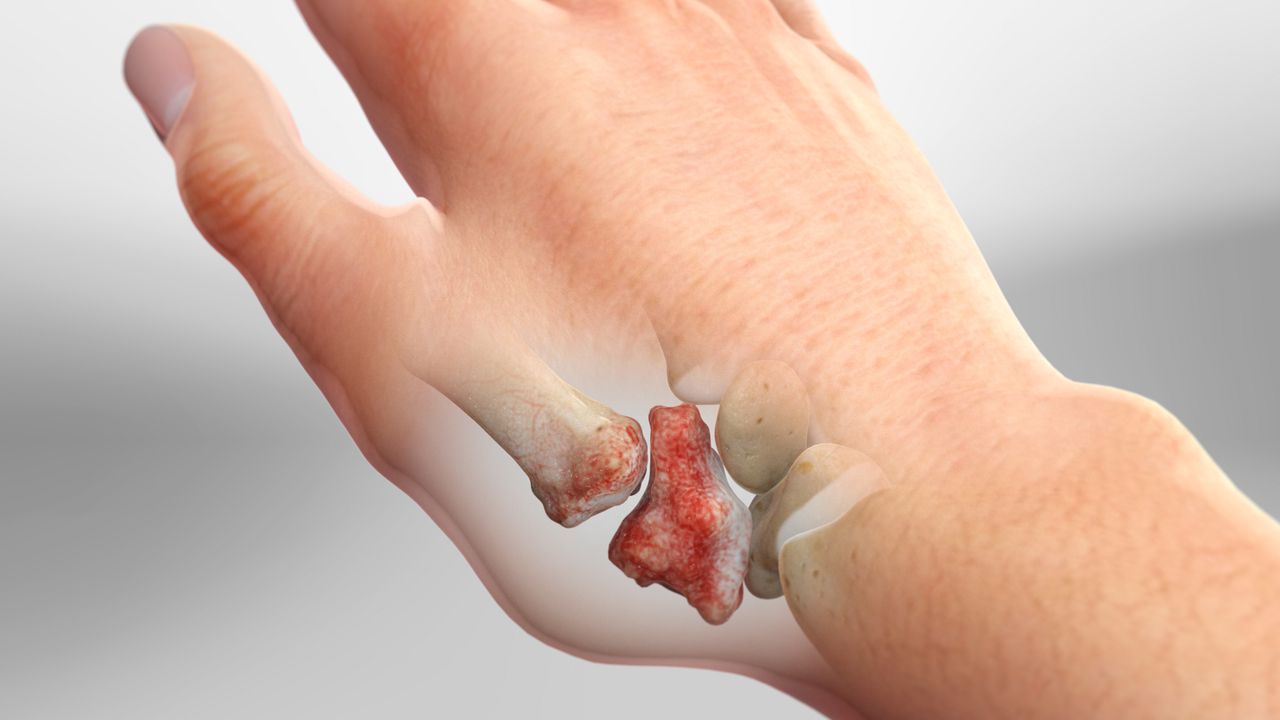
Understanding Arthritis in Thumb:
Types of Thumb Arthritis:
Thumb arthritis, a prevalent condition, encompasses various types like osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Each type presents distinct characteristics and requires tailored treatment approaches.
Common Symptoms and Diagnosis:
Recognizing Early Signs:
Early signs include pain, stiffness, and swelling at the base of the thumb. Limited range of motion may hinder grasping activities. Timely diagnosis is crucial for effective management.
Causes and Risk Factors:
Degenerative Factors:
Thumb arthritis often stems from degenerative processes, where the cartilage cushioning the joint gradually wears down. This wear and tear, coupled with aging, can contribute to arthritis development.
Genetic Predisposition:
Genetics play a role in the susceptibility to thumb arthritis. Individuals with a family history of arthritis are more likely to experience the condition.
Occupational Strain:
Repetitive hand movements and activities that exert stress on the thumb joint can increase the risk of developing arthritis. Certain occupations may contribute to this strain.
Prevention and Lifestyle Modifications:
Maintaining Joint Health:
Engage in hand-strengthening exercises and maintain a healthy weight to reduce strain on the thumb joint. Adequate rest between activities can prevent overuse.
Ergonomic Practices:
Adopt ergonomic tools and techniques to minimize thumb stress during daily tasks. Utilizing devices designed to ease strain can protect the joint.
Medical Treatment Options:
Pain Management Strategies:
Over-the-counter pain relievers and topical creams can alleviate discomfort. Consult a healthcare provider for appropriate options based on your condition.
Physical Therapy:
A physical therapist can design exercises to improve thumb mobility and strength. These exercises are tailored to individual needs.
Medications and Injections:
Anti-Inflammatory Medications:
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and manage pain associated with thumb arthritis.
Corticosteroid Injections:
Corticosteroid injections deliver anti-inflammatory medication directly to the affected joint, providing temporary relief from pain and swelling.
Surgical Interventions:
Joint Fusion:
For severe cases, joint fusion may be recommended. This surgical procedure involves fusing the bones of the thumb joint to reduce pain and improve stability.
Joint Replacement:
In advanced stages, joint replacement surgery can replace the damaged joint with an artificial implant, restoring thumb function and reducing pain.
Coping Strategies and Support:
Pain Management Techniques:
Explore relaxation techniques, mindfulness, and heat/cold therapy to manage pain and improve overall well-being.
Supportive Devices:
Thumb splints or braces can provide support and relief, especially during activities that strain the thumb joint.
Lifestyle Adaptations:
Activity Modifications:
Adjust daily activities to reduce strain on the thumb joint. Using assistive devices can help distribute stress away from the affected area.
Nutrition and Joint Health:
A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can promote joint health. Omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants are beneficial.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What causes arthritis in the thumb?
Thumb arthritis can be caused by wear and tear on the joint’s cartilage due to aging and genetic predisposition. Repetitive strain and certain occupations may also contribute.
2. What are the early symptoms of thumb arthritis?
Early signs include pain, stiffness, swelling, and limited range of motion at the base of the thumb. Difficulty gripping objects is also common.
3. Can thumb arthritis be prevented?
While prevention is challenging, maintaining a healthy weight, adopting ergonomic practices, and engaging in hand-strengthening exercises can reduce the risk.
4. How is thumb arthritis diagnosed?
Diagnosis involves a physical examination, medical history review, and possibly imaging tests like X-rays. Consulting a doctor is crucial for accurate diagnosis.
5. What are the treatment options for thumb arthritis?
Treatment ranges from lifestyle modifications, exercises, and pain management strategies to medications, injections, and, in severe cases, surgical interventions.
6. Can thumb arthritis be managed without surgery?
Yes, non-surgical options include medications, physical therapy, splints, and supportive devices. These approaches aim to alleviate pain and improve thumb function.
7. When is surgery recommended for thumb arthritis?
Surgery may be considered for severe cases where pain and impairment persist despite non-surgical treatments. Joint fusion or replacement are potential surgical options.
8. Are there coping strategies for managing thumb arthritis pain?
Yes, techniques like relaxation exercises, mindfulness, and heat/cold therapy can help manage pain. Using supportive devices during daily activities can also provide relief.
9. Can lifestyle adaptations improve thumb arthritis symptoms?
Yes, modifying daily activities to reduce thumb strain, using assistive devices, and maintaining a balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods can contribute to symptom management.
10. What’s the key to managing thumb arthritis effectively?
Early recognition of symptoms, seeking medical evaluation, and adopting a comprehensive approach that combines medical treatments, lifestyle changes, and supportive strategies are essential for effective management.
Conclusion
Managing arthritis in the thumb involves understanding symptoms, seeking early diagnosis, and adopting a multifaceted approach to treatment.




