Shoulder Labrum Tears: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Shoulder labrum tears can be a painful and debilitating condition that affects many individuals. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of shoulder labrum injuries, exploring their causes, symptoms, and effective treatment options. By understanding this common shoulder issue, you can take the necessary steps to alleviate pain and regain full shoulder mobility.
What Is the Shoulder Labrum?
The shoulder labrum is a vital structure within the shoulder joint that plays a crucial role in shoulder stability and function. It is a ring of cartilage that surrounds the socket of the shoulder joint, known as the glenoid. This cartilaginous ring deepens the socket, providing more stability to the shoulder and allowing a wide range of motion.
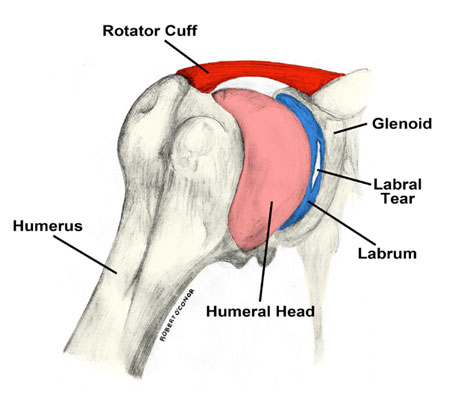
The labrum serves as an anchor point for the tendons and ligaments that hold the upper arm bone (humerus) in place. Without a healthy labrum, the shoulder joint becomes less stable, making it prone to dislocation and injury.
Common Shoulder Labrum Injuries
Shoulder labrum injuries encompass a range of conditions, but one of the most common is the labrum tear. These tears can occur in different areas of the labrum and vary in severity. Common causes of labrum tears include:
Trauma:
A direct blow to the shoulder or a fall on an outstretched arm can lead to labrum tears.
Repetitive Overhead Motions:
Athletes involved in sports like baseball, swimming, and weightlifting may develop labrum tears due to repetitive overhead motions.
Age-Related Wear and Tear:
As we age, the labrum can naturally degenerate, making it more susceptible to tears.
Symptoms of a Labrum Injury
Recognizing the symptoms of a shoulder labrum injury is essential for early diagnosis and treatment. Common signs of a labrum tear or injury include:
Shoulder Pain:
Persistent, aching pain in the shoulder joint, especially during certain movements or activities.
Catching Sensation:
You may experience a catching or popping sensation in the shoulder when moving it.
Weakness and Instability:
A labrum injury can lead to weakness in the affected arm and a feeling of shoulder instability.
Diagnosis of Labrum Injuries
Diagnosing shoulder labrum injuries typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, and imaging tests. Healthcare providers may perform tests to assess shoulder stability and identify the specific location and severity of the labrum injury. Common diagnostic methods include:
Physical Examination:
Your healthcare provider will perform a thorough examination of your shoulder, checking for pain, weakness, and range of motion.
Imaging Tests:
X-rays, MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), and CT (Computed Tomography) scans can provide detailed images of the shoulder joint and labrum, helping in accurate diagnosis.
Treatment Options
The treatment approach for shoulder labrum injuries depends on several factors, including the type and severity of the injury, the patient’s age, and their activity level. Here are common treatment options:
Conservative Management:
Rest and Activity Modification: For minor labrum tears, rest and avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms may be sufficient.
Physical Therapy: Physical therapists can develop exercises to strengthen the shoulder muscles and improve stability.
Medications: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can help reduce pain and inflammation.
Corticosteroid Injections:
In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be administered to alleviate pain and inflammation around the injured labrum.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Rehabilitation is a crucial phase of the recovery process following surgery or as part of conservative management. Physical therapy plays a central role in restoring shoulder strength, mobility, and stability. The rehabilitation program is tailored to each patient’s specific needs and may include:
Range of Motion Exercises: Gradual exercises to regain shoulder flexibility.
Strength Training: Targeted exercises to strengthen the shoulder muscles.
Proprioception Training: Improving the shoulder’s sense of position and stability.
Gradual Return to Activities: A phased approach to reintroducing sports or daily activities safely.
Prevention and Shoulder Health
Maintaining good shoulder health is essential for preventing labrum injuries. Consider these preventive measures:
Proper Warm-Up:
Always warm up before engaging in physical activities or sports that involve the shoulder.
Strength and Conditioning:
Include shoulder-strengthening exercises in your fitness routine.
Technique:
Ensure proper technique when lifting, throwing, or participating in sports.
Listen to Your Body:
Pay attention to any shoulder discomfort and seek medical advice if needed.
FAQ’s About shoulder labrum
1. Q: What is a shoulder labrum?
The shoulder labrum is a cartilage ring that surrounds the shoulder joint’s socket, providing stability and support to the shoulder.
2. Q: What causes a shoulder labrum tear?
Shoulder labrum tears can result from trauma, overuse, repetitive motions, or age-related wear and tear.
3. Q: What are the symptoms of a labrum tear?
Common symptoms include shoulder pain, catching or popping sensations, weakness, limited range of motion, and pain with activities.
4. Q: How is a labrum tear diagnosed?
Diagnosis often involves a physical examination, imaging tests (X-rays, MRI, CT scans), and sometimes arthroscopy for a closer look.
5. Q: Can labrum tears heal on their own?
Small tears may heal with conservative treatment, but more significant tears often require medical intervention.
6. Q: What are the treatment options for labrum tears?
Treatment options include rest, physical therapy, corticosteroid injections, or surgery, depending on the tear’s severity.
7. Q: Is surgery always necessary for a labrum tear?
Surgery is recommended for severe tears or when conservative methods don’t provide relief. Less severe tears may respond to non-surgical treatment.
8. Q: How long does the recovery process take after labrum surgery?
Recovery time varies but may take several months. Physical therapy is essential for a successful recovery.
9. Q: Can labrum injuries be prevented?
Preventive measures include proper warm-up, strengthening exercises, maintaining good technique, and listening to your body.
10. Q: What should I do if I suspect a labrum injury?
If you suspect a labrum injury or experience shoulder pain, consult with a healthcare professional for a proper evaluation and personalized treatment plan.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, shoulder labrum injuries, particularly labrum tears, can significantly impact shoulder function and quality of life. Understanding the causes, recognizing symptoms, and seeking timely medical evaluation are crucial steps in managing these injuries effectively. Whether through conservative measures, corticosteroid injections, or surgical intervention, there are options available to address shoulder labrum injuries. Additionally, proper rehabilitation and preventive strategies can help individuals regain strength, and mobility, and prevent future injuries.




