Stroke in the Eye Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
When it comes to strokes, many people associate them with the brain. However, there’s another type of stroke that affects the eye, known as “retinal artery occlusion” or simply “stroke in the eye.” This condition can lead to sudden vision loss and requires prompt attention. In this article, we’ll delve into the details of stroke in the eye, its causes, symptoms, and available treatments.
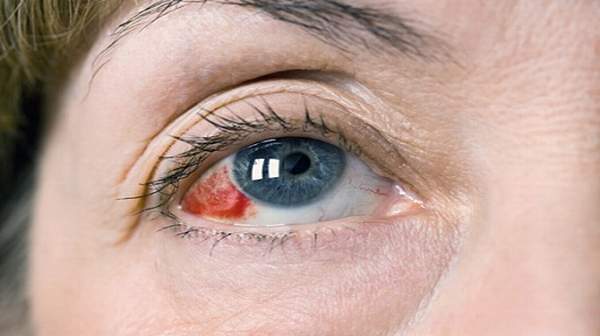
Understanding Retinal Artery Occlusion
Retinal artery occlusion (RAO) is a medical emergency that occurs when the blood flow to the retina is blocked. It’s often described as a “stroke in the eye” because it shares similarities with strokes that affect the brain. There are two main types of RAO: central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) and branch retinal artery occlusion (BRAO).
Central Retinal Artery Occlusion (CRAO):
In this condition, the central retinal artery, responsible for supplying blood to a large part of the retina, becomes blocked. This leads to severe and sudden vision loss in one eye.
Branch Retinal Artery Occlusion (BRAO):
In BRAO, one of the smaller branches of the central retinal artery is blocked. This results in vision loss in a specific area of the eye.
Causes of Eye Strokes
RAO occurs when something blocks the blood vessels that supply the retina. The most common causes include:
Blood Clots:
Small clots can travel through the bloodstream and block retinal arteries.
Cholesterol Plaques:
Fatty deposits in the arteries can lead to narrowing or blockages.
Underlying Medical Conditions:
Conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, and high cholesterol increase the risk of RAO.
Emboli:
Small particles, such as clots or plaques, can break free and lodge in retinal arteries, causing blockages.
Symptoms of Eye Strokes (RAO)
Recognizing the symptoms of an eye stroke is vital for seeking immediate medical attention. The following signs may indicate retinal artery occlusion:
Sudden Vision Loss:
The most prominent symptom is sudden and painless loss of vision in one eye. It often feels like a curtain or veil descending over the affected eye.
Blurred Vision:
Some individuals experience blurred or distorted vision in one eye.
Visual Field Defect:
Depending on whether it’s a central or branch artery occlusion, you may notice a loss of vision in the center or periphery of your visual field.
Color Vision Changes:
Colors may appear faded or washed out in the affected eye.
It’s crucial not to ignore these symptoms, as early intervention can make a significant difference in preserving your vision.
Diagnosis and Treatment
If you suspect you’re experiencing an eye stroke or have sudden vision changes, seek immediate medical attention. Eye care professionals can diagnose RAO through a comprehensive eye examination, including imaging tests like fluorescein angiography.
Treatment options may include:
Ocular Massage:
In some cases, gentle massage of the eye may help dislodge clots or emboli.
Medications:
Medications to lower eye pressure and improve blood flow may be administered.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy:
This involves breathing pure oxygen in a pressurized environment to increase oxygen delivery to the retina.
Intravenous Clot-Busting Medication:
Thrombolytic drugs can be used in certain cases to dissolve clots.
Laser Therapy:
This may be used to treat underlying conditions that contribute to RAO.
Prevention and Outlook
While some risk factors for RAO are beyond your control, you can take steps to reduce your risk:
Manage underlying medical conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes.
Maintain a healthy lifestyle, including regular exercise and a balanced diet.
Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
If you have risk factors, discuss preventive measures with your healthcare provider.
FAQs About stroke in the eye
Q: What is an eye stroke (retinal artery occlusion)?
A: An eye stroke, or retinal artery occlusion (RAO), is a condition where the blood flow to the retina is blocked, leading to sudden vision loss.
Q: What causes an eye stroke?
A: Eye strokes can be caused by the sudden blockage of retinal arteries, often due to blood clots or emboli. Underlying conditions like high blood pressure can contribute.
Q: What are the common symptoms of an eye stroke?
A: Common symptoms include sudden vision loss in one eye, blurred vision, visual field defects, and changes in color perception.
Q: Is an eye stroke painful?
A: No, eye strokes are typically painless, but they require immediate medical attention.
Q: How is an eye stroke diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis involves a comprehensive eye exam, including imaging tests like fluorescein angiography.
Q: Can an eye stroke cause permanent vision loss?
A: Yes, if not treated promptly, an eye stroke can result in permanent vision impairment or blindness.
Q: What are the risk factors for retinal artery occlusion?
A: Risk factors include high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, high cholesterol, and a history of blood clots.
Q: Can an eye stroke be prevented?
A: Prevention involves managing underlying conditions, leading a healthy lifestyle, and discussing preventive measures with a healthcare provider.
Q: What is the treatment for an eye stroke?
A: Treatment options may include medications, ocular massage, hyperbaric oxygen therapy, intravenous clot-busting drugs, and laser therapy.
Q: What should I do if I experience symptoms of an eye stroke?
A: Seek immediate medical attention if you experience sudden vision changes, as early intervention is crucial for better outcomes.
Conclusion:
A stroke in the eye, or retinal artery occlusion, is a serious condition that demands immediate attention. Understanding its causes, symptoms, and risk factors is crucial for prevention and early treatment. By recognizing the signs and seeking prompt medical care, you can maximize the chances of preserving your vision.




