The Enigma: Synovial Sarcoma – Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
What is Synovial Sarcoma?
Synovial sarcoma is a rare type of cancer that primarily affects the soft tissues around joints, such as the arms, legs, or neck. Despite its name, it doesn’t originate from the synovium, which is the lining of joints. Instead, it tends to develop near large joints, giving it its name. While synovial sarcoma accounts for only about 5-10% of all soft tissue sarcomas, understanding this cancer is crucial due to its potential aggressiveness and impact on affected individuals.
Prevalence and Rarity
Synovial sarcoma is considered rare in the realm of cancers. According to recent medical data, it accounts for approximately 5-10% of all soft tissue sarcomas. This rarity can make diagnosis and treatment more challenging, as many healthcare professionals may not encounter it frequently. However, its relative scarcity doesn’t diminish its significance. Awareness and understanding are key to early detection and improved outcomes.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection is critical in managing synovial sarcoma effectively. Like many cancers, synovial sarcoma is easier to treat when detected in its early stages. Unfortunately, its symptoms can be vague and mimic other less serious conditions, which may delay diagnosis. This article aims to shed light on the signs, symptoms, and diagnostic methods associated with synovial sarcoma, emphasizing the importance of early detection for a more favorable prognosis.
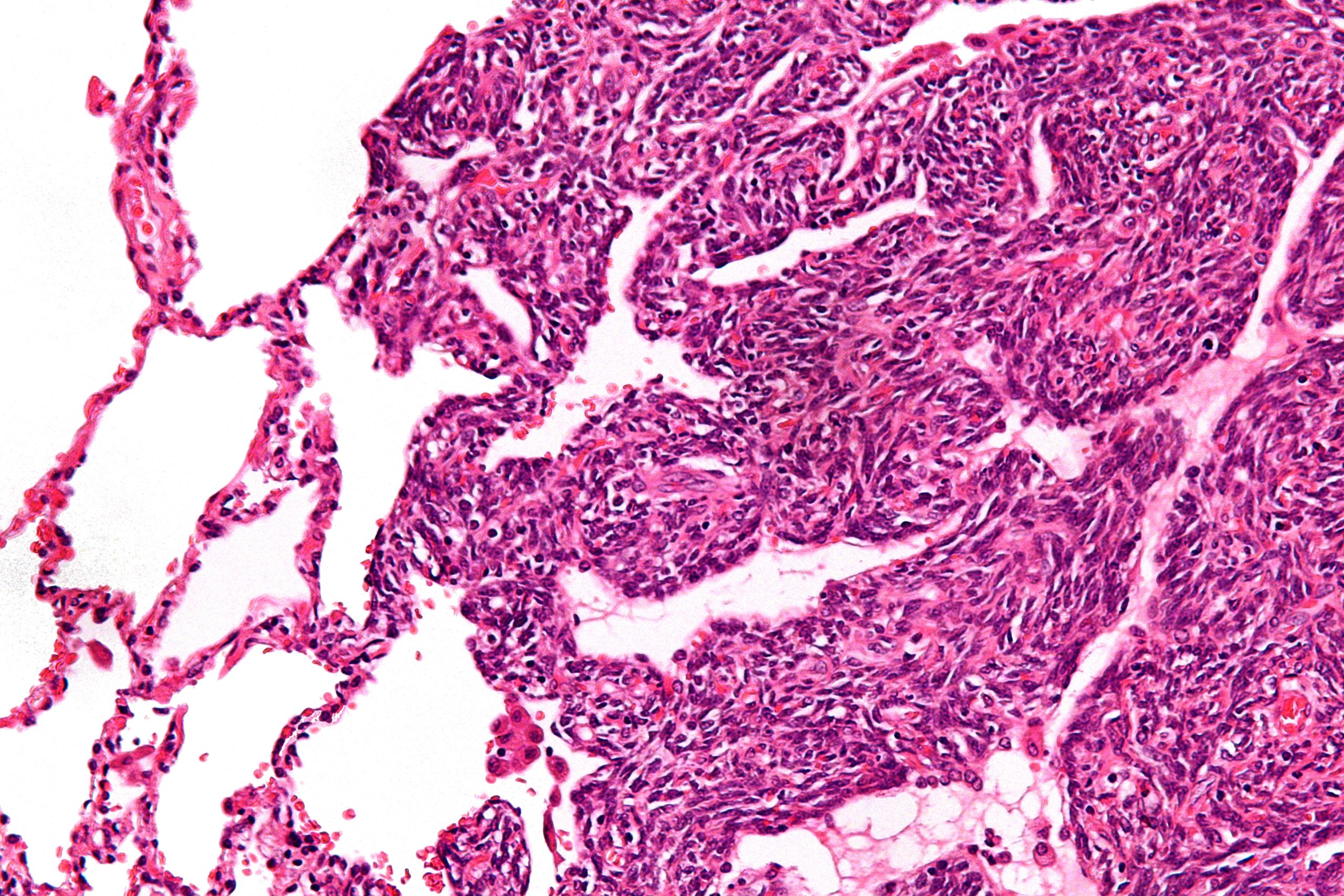
Understanding Synovial Sarcoma
Definition and Origins
Synovial sarcoma is a malignancy that arises in the soft tissues, but it’s important to clarify that it doesn’t originate from the synovial membrane, as its name might suggest. Instead, it usually develops close to the large joints, such as the knee or ankle. This cancer is characterized by the abnormal growth of cells in the connective tissues, and it often presents as a painless lump or swelling.
Types of Synovial Sarcoma
There are different subtypes of synovial sarcoma, with the most common being biphasic and monophasic. Biphasic synovial sarcoma consists of two types of cells: spindle cells and epithelial cells. Monophasic synovial sarcoma, on the other hand, predominantly consists of spindle cells. Understanding these subtypes is crucial because they may influence the course of treatment and prognosis.
Who is at Risk?
While synovial sarcoma can affect individuals of all ages, it most commonly appears in young adults and adolescents. There is no specific gender predilection, meaning it can occur in both males and females. Additionally, individuals with a family history of sarcomas or genetic predisposition may have an increased risk. Recognizing these risk factors can help individuals and healthcare providers remain vigilant and proactive in monitoring for this rare cancer.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Common Symptoms
Identifying synovial sarcoma can be challenging because its symptoms are often nonspecific. Some common signs to watch for include the presence of a painless lump or swelling near a joint, joint stiffness, and limited mobility. Other possible symptoms include localized pain, fatigue, fever, and unexplained weight loss. If you or a loved one experience these symptoms, it’s essential to seek medical evaluation promptly.
How is it Diagnosed?
Diagnosing synovial sarcoma typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, imaging studies (such as MRI or CT scans), and, in most cases, a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis. The biopsy allows for the examination of tissue samples under a microscope to identify the unique characteristics of synovial sarcoma cells. Early and accurate diagnosis is vital for developing an effective treatment plan.
Importance of Early Diagnosis
Early detection of synovial sarcoma significantly improves treatment outcomes. When diagnosed in its early stages, before it spreads to other parts of the body, it is more likely to be treatable with less aggressive interventions. This underscores the importance of promptly consulting with a healthcare professional if you suspect any symptoms related to synovial sarcoma.
Causes and Risk Factors
Genetic Predisposition
While the exact cause of synovial sarcoma remains unclear, there is evidence suggesting a genetic predisposition may play a role. Some individuals may carry genetic mutations that make them more susceptible to developing this rare cancer. Research into these genetic factors is ongoing and may provide insights into both causation and prevention.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors are also being explored in relation to synovial sarcoma. Some studies have examined potential links between exposure to certain chemicals or toxins and an increased risk of developing this cancer. However, more research is needed to establish concrete connections. It’s essential to stay informed about emerging findings in this area.
Recent Research Findings
Ongoing research is shedding light on the complex mechanisms behind synovial sarcoma. Scientists are delving deeper into the genetic and molecular underpinnings of this cancer, with the aim of identifying potential therapeutic targets. Stay tuned for the latest breakthroughs in synovial sarcoma research as they have the potential to revolutionize treatment approaches.
Treatment Options
Surgery
Surgery is often the primary treatment for synovial sarcoma. The goal is to remove the tumor and a margin of healthy tissue to ensure that no cancer cells remain. The extent of surgery may vary based on the tumor’s size, location, and whether it has spread. Advances in surgical techniques have improved outcomes and reduced the impact on a patient’s quality of life.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy is commonly used in conjunction with surgery or as a standalone treatment. It involves using high-energy rays to target and destroy cancer cells. This therapy may be administered before surgery to shrink the tumor, after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells, or to relieve pain and control symptoms in cases where surgery isn’t feasible.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is sometimes recommended for synovial sarcoma, especially when the cancer has spread or if it’s not possible to remove the entire tumor through surgery. Chemotherapy drugs circulate throughout the body, targeting cancer cells. The specific drugs and treatment regimen will be determined by the oncologist based on the patient’s individual case.
Targeted Therapy
Recent advancements in cancer treatment have led to the development of targeted therapies for synovial sarcoma. These drugs are designed to specifically target the molecular abnormalities present in the cancer cells. Targeted therapy offers the potential for more effective treatment with fewer side effects compared to traditional chemotherapy.
Emerging Treatments
The landscape of synovial sarcoma treatment is continuously evolving. Researchers are exploring innovative therapies, including immunotherapy and precision medicine approaches, to improve outcomes for patients. Staying informed about these emerging treatments is essential for individuals and their healthcare providers.
Living with Synovial Sarcoma
Coping Strategies
A synovial sarcoma diagnosis can be emotionally and physically challenging. Coping strategies play a crucial role in managing the psychological and emotional aspects of living with this condition. Patients and their support networks should explore counseling, support groups, and mindfulness techniques to help navigate the journey.
Support Networks
Building a strong support network is invaluable when living with synovial sarcoma. Friends, family, and support groups can provide emotional support, share experiences, and offer practical assistance. Connecting with others who have faced similar challenges can provide comfort and valuable insights.
Survivor Stories
Reading about the experiences of synovial sarcoma survivors can be inspiring and educational. These stories offer hope and practical insights into living with the condition. Survivor stories can also provide a sense of community and encouragement for individuals currently battling synovial sarcoma.
Prognosis and Survival Rates
Factors Affecting Prognosis
The prognosis for synovial sarcoma varies depending on several factors. These include the tumor’s size, location, subtype, and the extent of its spread. Additionally, the patient’s overall health and response to treatment play significant roles in determining the outlook. Discussing prognosis with an oncologist is essential for understanding individual circumstances.
Latest Survival Rate Statistics
Survival rates for synovial sarcoma have improved over the years due to advances in treatment. Providing the latest survival rate statistics can help patients and their families gain a realistic understanding of what to expect. However, it’s crucial to remember that statistics are generalizations and may not reflect individual outcomes.
Advances in Synovial Sarcoma Research
Current Studies and Clinical Trials
Ongoing research is a beacon of hope for individuals with synovial sarcoma. Current studies and clinical trials are exploring novel treatments and therapies. Patients and their healthcare teams may consider participation in clinical trials as a way to access cutting-edge treatments and contribute to the advancement of medical knowledge.
NLP in Medical Research
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is playing an increasingly important role in medical research, including the study of synovial sarcoma. NLP techniques are used to analyze vast amounts of medical literature and patient data, aiding in the discovery of patterns and insights. Staying informed about NLP’s role in medical research can help patients and healthcare professionals access the latest information.
Prevention and Awareness
Prevention Strategies
Currently, there are no known foolproof methods for preventing synovial sarcoma since its exact cause is still under investigation. However, staying informed about potential risk factors, such as genetic predisposition or environmental exposures, is important. Individuals with a family history of sarcomas may consider genetic counseling for early detection and monitoring.
Raising Awareness
Raising awareness about synovial sarcoma is vital to its early detection and better outcomes. Encouraging regular check-ups, especially if there’s a family history or known risk factors, can help catch this rare cancer in its early stages. Supporting organizations dedicated to synovial sarcoma research and patient advocacy can also contribute to increased awareness.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Synovial Sarcoma
What is synovial sarcoma?
Synovial sarcoma is a rare form of cancer that affects the soft tissues, often occurring near joints in the arms, legs, or neck. Despite its name, it doesn’t originate from the synovium.
Who is at risk of developing synovial sarcoma?
Synovial sarcoma can affect individuals of all ages but is most commonly seen in young adults and adolescents. There is no specific gender predilection.
What are the common symptoms of synovial sarcoma?
Symptoms may include the presence of a painless lump or swelling near a joint, joint stiffness, limited mobility, localized pain, fatigue, fever, and unexplained weight loss.
How is synovial sarcoma diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically involves a combination of medical history review, physical examination, imaging studies (e.g., MRI, CT scans), and a biopsy to confirm the diagnosis.
What are the treatment options for synovial sarcoma?
Treatment may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, or a combination of these depending on the tumor’s size, location, and subtype.
Are there different types of synovial sarcoma?
Yes, there are subtypes of synovial sarcoma, with biphasic and monophasic being the most common. Biphasic consists of spindle and epithelial cells, while monophasic is predominantly spindle cells.
What factors affect the prognosis of synovial sarcoma?
Prognosis varies based on factors like tumor size, location, subtype, spread, overall health, and response to treatment.
Are there any prevention strategies for synovial sarcoma?
Currently, there are no known prevention strategies due to the uncertain causes. However, individuals with a family history may consider genetic counseling.
Where can I find support if I or a loved one is diagnosed with synovial sarcoma?
Support networks, counseling, and synovial sarcoma support groups can provide emotional support and practical guidance.
What’s the latest research on synovial sarcoma?
Ongoing research explores new treatments, including immunotherapy and precision medicine. Staying informed about clinical trials and advancements is essential for those affected by synovial sarcoma.
Conclusion:
Synovial sarcoma, though rare, is a cancer that demands attention and understanding. This article has explored its definition, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment options, and the importance of early detection. It has also touched on ongoing research, coping strategies, and support for those living with synovial sarcoma.




