Demystifying Apolipoprotein B: The Key Player in Cholesterol Management
In the world of cardiovascular health, Apolipoprotein B (ApoB) stands as a crucial player. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricate role of Apolipoprotein B, shedding light on its significance in cholesterol management and overall heart health.
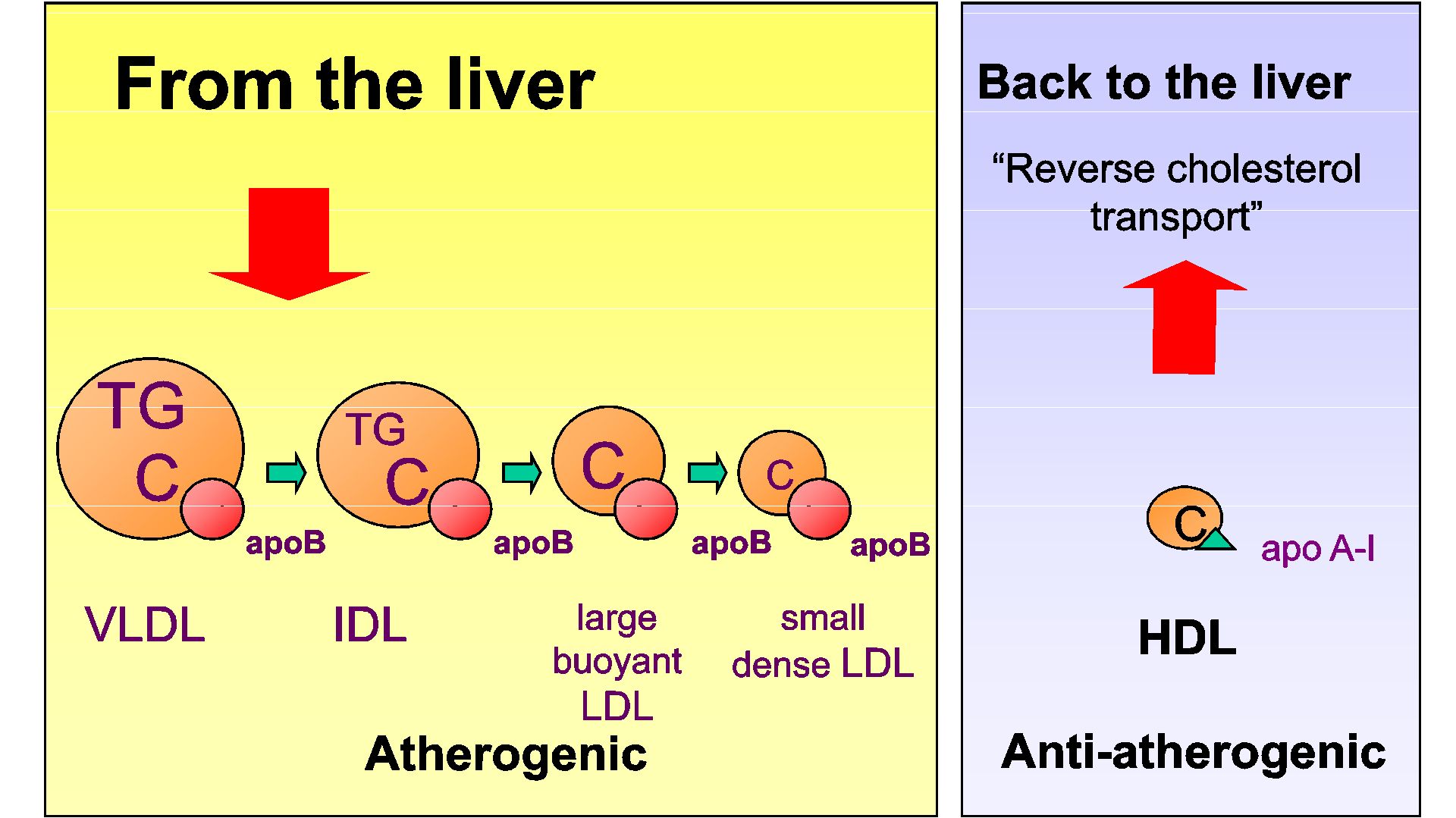
What Is Apolipoprotein B?
At its core, Apolipoprotein B is a protein that plays a pivotal role in the transportation of lipids (fats) throughout your body. It’s primarily associated with Low-Density Lipoprotein (LDL), often referred to as “bad cholesterol.” Let’s explore ApoB’s role in cholesterol metabolism and how it influences your cardiovascular well-being.
Apolipoprotein B and Cholesterol Metabolism
Apolipoprotein B’s main responsibility is to facilitate the transportation of lipids, including cholesterol, in your bloodstream. To grasp its importance, it’s essential to understand how ApoB interacts with lipoproteins like LDL.
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) is a lipoprotein that carries cholesterol from your liver to various cells in your body. Apolipoprotein B is a structural protein present on the surface of LDL particles, serving as a key identifier for cells that require cholesterol. This interaction allows LDL to deliver cholesterol to cells for various essential functions.
The Significance of Apolipoprotein B in Cardiovascular Health
Apolipoprotein B and Atherosclerosis
One of the most critical aspects of Apolipoprotein B’s role in cardiovascular health is its connection to atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of cholesterol-rich plaques in the arteries. Here’s how ApoB contributes to this process:
Apolipoprotein B-containing lipoproteins, primarily LDL, play a central role in the formation of atherosclerotic plaques. When LDL cholesterol levels are elevated, there is an increased influx of cholesterol into the artery walls. Apolipoprotein B molecules guide LDL particles into the arterial walls, where they can accumulate and trigger inflammation, leading to plaque formation.
Apolipoprotein B Testing and Interpretation
Now that we’ve explored Apolipoprotein B’s significance in cardiovascular health, let’s delve into ApoB testing and how to interpret the results:
Apolipoprotein B blood tests measure the concentration of ApoB in your bloodstream. This measurement provides valuable insights into your cardiovascular risk. When interpreting Apolipoprotein B test results:
Normal Range:
The normal range for ApoB levels can vary slightly between laboratories. Your healthcare provider will compare your results to established reference ranges.
Elevated ApoB Levels:
Higher-than-normal ApoB levels may indicate an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, particularly atherosclerosis. It suggests that there is an excess of ApoB-containing lipoproteins in your bloodstream, which can contribute to plaque formation.
Risk Assessment:
Your healthcare provider will consider your ApoB levels along with other cardiovascular risk factors, such as LDL cholesterol levels, blood pressure, and family history. This comprehensive assessment helps determine your overall risk and guides treatment decisions.
Treatment Guidance:
Elevated ApoB levels may prompt your healthcare provider to recommend lifestyle modifications, such as dietary changes and increased physical activity. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to lower ApoB levels and reduce cardiovascular risk.
Managing Apolipoprotein B Levels
Lifestyle Interventions to Lower Apolipoprotein B
Lowering elevated Apolipoprotein B levels is essential for reducing cardiovascular risk. Fortunately, several lifestyle modifications can help you achieve this:
Dietary Changes:
Adopt a heart-healthy diet that focuses on reducing saturated fats, trans fats, and dietary cholesterol. Emphasize foods rich in soluble fiber, such as oats, beans, and fruits, which can help lower ApoB levels.
Regular Exercise:
Engage in regular physical activity to improve your lipid profile. Aerobic exercises like walking, jogging, and swimming can contribute to reducing Apolipoprotein B levels.
Weight Management:
Maintaining a healthy weight or losing excess weight can positively impact your ApoB levels. Even modest weight loss can lead to improvements in your lipid profile.
Moderate Alcohol Consumption:
If you consume alcohol, do so in moderation. Limiting alcohol intake can help manage Apolipoprotein B levels.
Statins:
These medications are commonly prescribed to lower LDL cholesterol levels and, by extension, Apolipoprotein B levels.
Fibrates:
Fibrates are another class of medications that can help reduce ApoB-containing lipoproteins.
Nutritional Supplements:
Omega-3 fatty acid supplements, such as fish oil, may have a modest effect on ApoB levels.
The Latest Research and Developments
Emerging Insights into Apolipoprotein B
Ongoing research continues to uncover new insights into the role of Apolipoprotein B in cardiovascular health. Here are some recent findings and developments:
Genetic Studies:
Genetic research has identified specific genetic variants associated with Apolipoprotein B metabolism, shedding light on individual differences in ApoB levels and cardiovascular risk.
Therapeutic Advances:
Researchers are exploring novel therapies and drugs aimed at targeting Apolipoprotein B to reduce cardiovascular risk further.
Precision Medicine:
The field of precision medicine is evolving, allowing healthcare providers to tailor treatments based on an individual’s unique genetic and metabolic profile, including ApoB levels.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What does Apolipoprotein B do in the body?
Apolipoprotein B plays a key role in transporting cholesterol and fats in the bloodstream, contributing to both cardiovascular health and risk.
What are normal Apolipoprotein B levels?
Normal ApoB levels can vary, but they are generally below 90 mg/dL. It’s essential to interpret results in the context of your overall cardiovascular risk.
Can I lower my Apolipoprotein B levels through diet alone?
While diet plays a significant role, some individuals may require medications or therapies to achieve optimal ApoB levels.
Are there natural ways to reduce ApoB levels?
Yes, natural approaches include dietary changes, exercise, and weight management. Consult your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
Can elevated ApoB levels be a genetic issue?
Yes, genetics can influence Apolipoprotein B levels. Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to higher ApoB levels.
What are the risks of elevated ApoB levels?
Elevated ApoB levels are associated with an increased risk of atherosclerosis, heart disease, and stroke.
How often should I have my Apolipoprotein B levels tested?
The frequency of testing may vary based on your risk factors and your healthcare provider’s recommendations. Regular monitoring is essential for managing cardiovascular risk.
Do medications for lowering LDL cholesterol also lower Apolipoprotein B?
Yes, medications like statins are effective in reducing both LDL cholesterol and ApoB levels.
Are there dietary supplements that can help lower ApoB levels?
Omega-3 fatty acid supplements, such as fish oil, may have a modest effect on ApoB levels. However, consult your healthcare provider before taking supplements.
Is Apolipoprotein B the same as LDL cholesterol?
No, Apolipoprotein B is a protein present on the surface of LDL particles. While they are related, they are not the same, and measuring both provides a more comprehensive assessment of cardiovascular risk.
Conclusion:
In the quest for optimal cardiovascular health, Apolipoprotein B emerges as a central figure. Its role in cholesterol metabolism and its influence on heart disease risk cannot be overstated. ApoB is a protein that guides lipoproteins, including LDL cholesterol, in your bloodstream. It plays a pivotal role in cholesterol transportation and metabolism.




