Understanding Flu Contagiousness: How Long Is the Flu Contagious?
In the realm of infectious diseases, the flu (influenza) holds a prominent place. As a viral respiratory illness, the flu can swiftly spread from person to person, leading to community outbreaks and seasonal epidemics. A critical aspect of managing flu transmission is understanding its contagiousness and how long individuals remain capable of spreading the virus to others.
The Basics of Influenza Contagion:
Influenza viruses primarily spread through tiny droplets released into the air when an infected person talks, coughs, or sneezes. These droplets can be inhaled by individuals nearby or land on surfaces, where they can survive for a certain period. The virus can then be transmitted when a person touches these surfaces and subsequently touches their mouth, nose, or eyes.
Given its mode of transmission, the flu can easily find its way into homes, workplaces, schools, and public spaces. Understanding how long the flu remains contagious is crucial for minimizing its impact on public health.
Flu Contagious Period: What to Expect:
The contagious period of the flu refers to the span during which an infected individual can transmit the virus to others. This period typically starts before symptoms become evident and continues until the individual recovers.
While the duration of contagiousness varies from person to person, it generally centers around the initial days of illness. During this time, the concentration of the virus in respiratory secretions is usually at its highest. This is why people are often advised to stay home and limit contact with others when experiencing flu-like symptoms.
Early Stages: Initial Contagiousness:
In the early stages of flu onset, individuals tend to be most contagious. This initial contagiousness can begin even before symptoms fully develop. Consequently, a person may unknowingly spread the virus to others before realizing they are sick.
Common symptoms that might signal the onset of contagiousness include fever, chills, body aches, fatigue, and a sore throat. As these symptoms manifest, the individual becomes increasingly capable of transmitting the virus to close contacts.
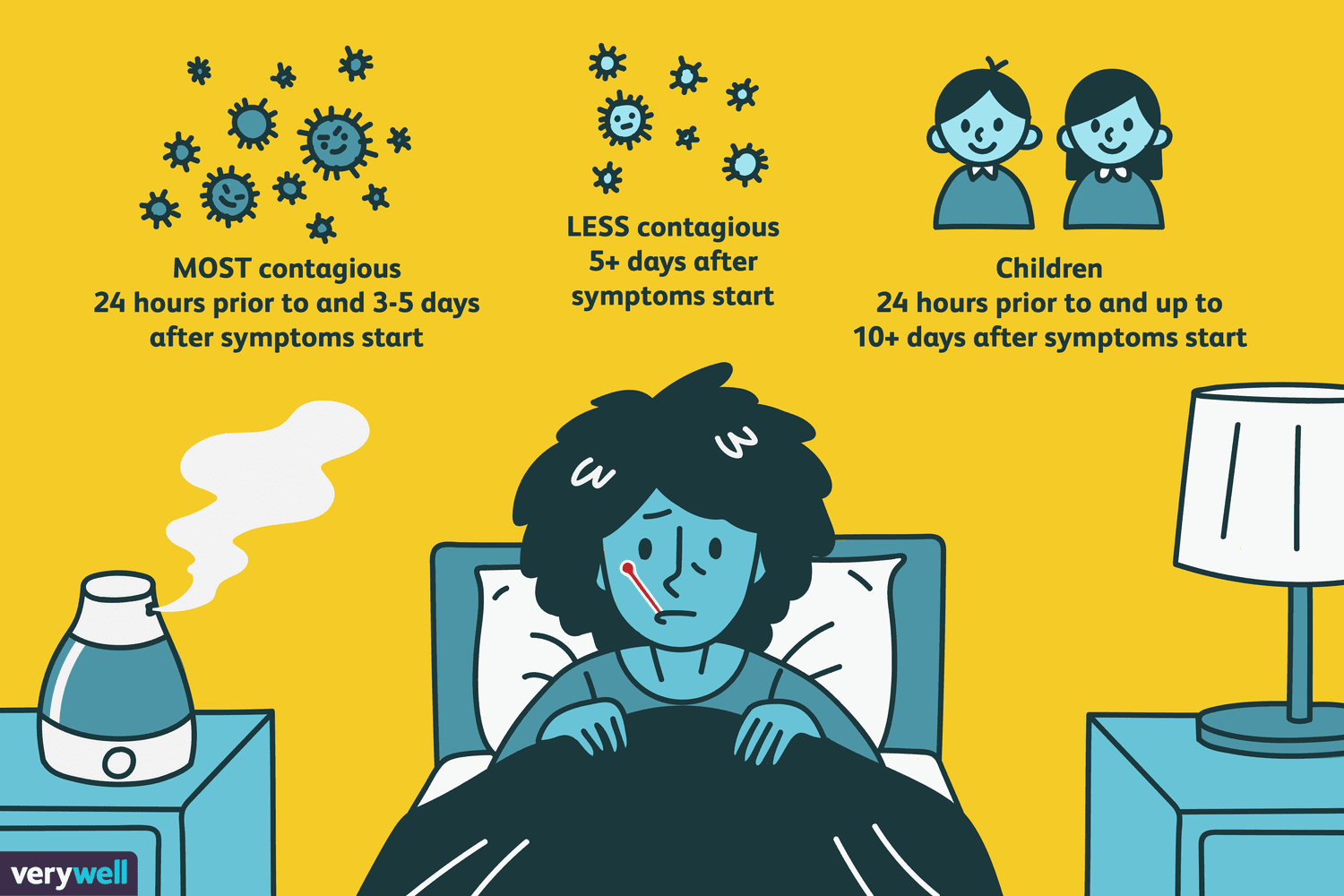
Peak Contagiousness: The First Few Days:
As the flu progresses, the contagiousness tends to peak during the first 1 to 3 days of symptoms. This is when the viral load in respiratory secretions is at its highest, and the potential for transmission is greatest. Activities like coughing, sneezing, and even talking can release a substantial number of virus-laden droplets into the surrounding environment.
During this period, individuals should exercise extra caution to avoid close contact with others, especially those who may be more vulnerable to severe flu complications.
Contagiousness Duration: 5-7 Days:
While the peak contagiousness occurs within the first few days, the overall duration of flu contagiousness spans approximately 5 to 7 days from the onset of symptoms. It’s important to note that even as symptoms start to improve, individuals can still shed the virus and remain capable of transmitting it to others.
Factors like age, overall health, and the specific flu strain can influence how long someone remains contagious. It’s advised to err on the side of caution and consider the full 5 to 7-day window when determining when it’s safe to resume normal activities.
Reducing Contagiousness Risk: Precautions and Hygiene:
Minimizing the spread of the flu requires adopting preventive measures and practicing good hygiene. Some practical steps to reduce contagiousness risk include:
Isolation:
Stay home when feeling unwell, especially during the peak contagious period.
Cover Coughs and Sneezes:
Use tissues or your elbow to cover your mouth and nose when coughing or sneezing.
Hand Hygiene:
Wash hands frequently with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, or use hand sanitizer if soap is unavailable.
Avoid Close Contact:
Keep a safe distance from others, especially those who may be more susceptible to severe flu outcomes.
When Can You Return to Normal Activities?
A common concern is knowing when it’s safe to return to work, school, or other activities after having the flu. To make an informed decision, consider the following guidelines:
Fever-Free:
Wait at least 24 hours after your fever has subsided without the use of fever-reducing medications.
Improved Symptoms:
Ensure that your symptoms have significantly improved, including cough and shortness of breath.
Energy Levels:
Regain sufficient energy levels to engage in daily tasks without overexertion.
Vulnerable Groups and Prolonged Contagiousness:
It’s important to note that certain groups, such as young children, older adults, and individuals with weakened immune systems, may remain contagious for a more extended period. For these vulnerable populations, it’s advisable to exercise extra caution and extend the period of isolation to prevent further transmission.
Post-Recovery: Lingering Contagiousness:
Even after symptoms subside and an individual starts feeling better, it’s possible to continue shedding the virus for a limited time. Taking continued precautions, such as maintaining good hygiene and avoiding close contact, can help prevent the spread of the virus to others.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Flu Contagiousness
1. How long is the flu contagious after symptoms start?
The flu is most contagious during the first 1 to 3 days of symptoms. However, you can remain contagious for about 5 to 7 days from the onset of symptoms.
2. Can you spread the flu before showing symptoms?
Yes, you can spread the flu virus before symptoms fully develop. This is why it’s important to practice preventive measures even if you feel fine.
3. Are children more contagious than adults during the flu?
Children, especially young ones, might shed the flu virus for longer periods than adults. They can remain contagious even after symptoms improve.
4. Is it safe to return to work or school once symptoms subside?
Wait at least 24 hours after your fever subsides without fever-reducing medications. Ensure that other symptoms have significantly improved too.
5. Can you still be contagious if you’re on antiviral medication?
Antiviral medications can reduce the duration of contagiousness, but you may still be capable of spreading the virus until the prescribed course is completed.
6. Are there cases where people remain contagious longer than a week?
Yes, vulnerable individuals, such as those with weakened immune systems, might remain contagious for an extended period. It’s important to exercise caution.
7. Does the type of flu strain affect the contagious period?
Different flu strains can impact the contagious period. It’s best to consider the general 5 to 7-day guideline but be cautious if symptoms persist.
8. How can I protect my family from getting the flu from me?
Practice good hygiene, isolate yourself when symptomatic, and avoid close contact. These measures can help prevent transmission to family members.
9. Can I spread the flu after I feel better?
Yes, you might continue shedding the virus even after symptoms improve. Continue practicing hygiene and avoid close contact to prevent spreading.
10. Can I go out in public if I’m still coughing after the flu?
It’s recommended to avoid public spaces until your cough significantly improves. Coughing can release virus-laden droplets, potentially infecting others.
Conclusion:
Understanding the timeline of flu contagiousness is essential for both personal health and public well-being. By recognizing the peak contagious period and taking preventive measures, individuals can play an active role in minimizing the spread of the flu within their communities. Remember, responsible contagion management benefits everyone’s health and contributes to a healthier society.




