Unmasking the Mystery: Sports Hernia Explained
As athletes push their bodies to the limit, they often encounter a range of injuries. Among these, sports hernia stands out as a particularly challenging adversary. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve deep into the world of sports hernia to shed light on what it is, how it affects athletes, and what can be done to prevent and treat it.
Understanding Sports Hernia
To grasp the intricacies of sports hernia, it’s crucial to distinguish it from a traditional hernia. Unlike the more common inguinal hernia, sports hernia primarily involves the soft tissues of the groin and lower abdominal region. It is not characterized by a visible bulge but rather by elusive and persistent groin pain.
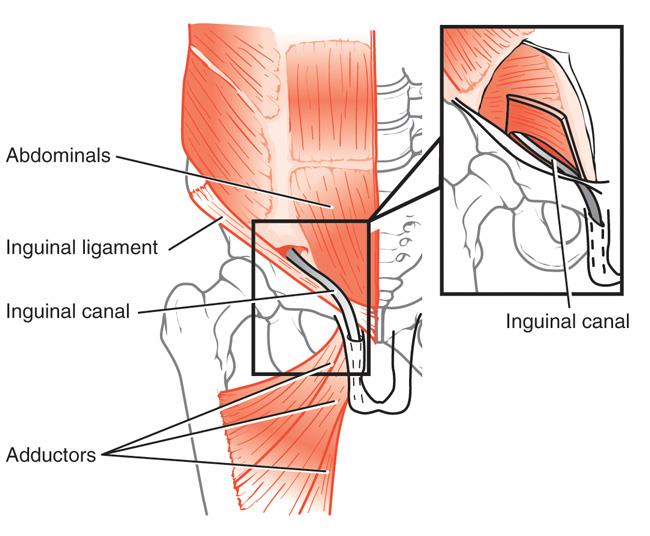
A sports hernia, also known as athletic pubalgia, occurs due to the tearing or stretching of the muscles and tendons in the groin area. It is often associated with sports that involve sudden changes in direction, twisting movements, and repetitive stress on the pelvic region. Understanding the anatomy involved in this condition is essential to comprehend its impact fully.
Common Symptoms of Sports Hernia
Recognizing sports hernia relies on identifying its characteristic symptoms. While it may not manifest as a conspicuous lump, the discomfort it inflicts on athletes is unmistakable. Common symptoms include:
Groin Pain:
The hallmark of sports hernia is persistent groin pain, typically on one side. The pain can be sharp, stabbing, or a dull ache, often worsening during physical activity.
Tenderness:
Athletes with a sports hernia often experience tenderness in the affected area, especially when pressure is applied.
Discomfort During Exercise:
Engaging in sports or strenuous activities can exacerbate the pain, making it challenging for athletes to perform at their best.
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the origins of sports hernia is key to prevention and early intervention. This section delves into the root causes and risk factors that contribute to the development of sports hernia.
A sports hernia often arises due to:
Repetitive Stress:
Sports that involve frequent twisting and turning, such as soccer, hockey, and tennis, place repetitive stress on the lower abdomen and pelvic region.
Sudden Movements:
The abrupt, explosive movements required in many sports, like sprinting or changing direction swiftly, can strain the groin muscles and tendons.
Weak Muscles:
Inadequate core muscle strength, particularly in the lower abdomen and pelvis, can make athletes more susceptible to sports hernia.
Diagnosing Sports Hernia
Diagnosing sports hernia requires a combination of physical examinations, medical history assessment, and imaging tests. This section explores the diagnostic process, emphasizing the importance of seeking professional medical evaluation when symptoms arise.
The diagnostic journey may include:
Physical Examination:
A healthcare provider will conduct a thorough physical examination, focusing on the groin area, to assess tenderness and discomfort.
Medical History:
Sharing your medical history, including previous injuries and activity levels, helps in the diagnostic process.
Treatment Options
For athletes facing the challenge of sports hernia, a range of treatment options is available. This section elucidates these options, highlighting the importance of personalized treatment plans tailored to individual needs.
Treatment may include:
Rest and Activity Modification:
Rest is often the first step in healing. Athletes may need to modify or temporarily cease their training routines.
Physical Therapy:
A structured physical therapy program can help strengthen the core muscles, improve flexibility, and facilitate recovery.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Recovery from sports hernia is a critical phase for athletes aiming to return to their peak performance levels. This section guides athletes through the recovery process, emphasizing the importance of rehabilitation.
The recovery journey often involves:
Rehabilitation Exercises:
A structured rehabilitation program typically includes exercises to strengthen the core, improve flexibility, and gradually reintroduce sports-specific movements.
Restoration of Functionality:
Athletes work closely with physical therapists to regain full functionality and range of motion.
Prevention and Injury Reduction
Preventing sports hernia is a top priority for athletes. In this section, we provide strategies to reduce the risk of developing this challenging condition.
Preventive measures include:
Core Strengthening:
Implementing a consistent core strengthening regimen can enhance the stability of the pelvic region.
Proper Warm-Up:
Adequate warm-up and stretching before sports activities can prepare the muscles for exertion.
Athlete Testimonials and Experiences
Real-life experiences from athletes who have faced sports hernia can provide valuable insights and inspiration. In this section, we share personal stories and testimonials to add authenticity and relatability to the article.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) about Sports Hernia
1. Q: What is a sports hernia?
A: A sports hernia, also known as athletic pubalgia, is a painful condition characterized by the tearing or stretching of muscles and tendons in the groin and lower abdominal area.
2. Q: What causes sports hernia in athletes?
A: Sports hernia is often caused by repetitive stress, sudden movements, and intense physical activities commonly associated with sports.
3. Q: What are the primary symptoms of sports hernia?
A: Common symptoms include groin pain, tenderness, discomfort during physical activity, and difficulty with everyday movements.
4. Q: Is a sports hernia the same as a traditional hernia?
A: No, a sports hernia primarily involves soft tissues in the groin area, while a traditional hernia typically involves a protrusion of abdominal organs through a weakened abdominal wall.
5. Q: How is sports hernia diagnosed?
A: Diagnosis may involve physical examinations, medical history assessment, and imaging tests like MRI or ultrasound to visualize the affected area.
6. Q: What are the treatment options for sports hernia?
A: Treatment can include rest, physical therapy, and, in some cases, surgical intervention to repair damaged muscles and tendons.
7. Q: How long does it take to recover from a sports hernia?
A: Recovery times vary but may involve a period of rest, followed by a structured rehabilitation program that can last several weeks to months.
8. Q: Can sports hernia be prevented?
A: Yes, preventive measures include core strengthening, proper warm-up, balanced training, and attentive monitoring of the body’s signals.
9. Q: Can athletes return to their sports after recovering from a sports hernia?
A: Yes, many athletes can return to their sports after successful treatment and rehabilitation, provided they follow a gradual and monitored return.
10. Q: Are there any long-term complications of sports hernia?
A: In most cases, with appropriate treatment and rehabilitation, athletes can recover fully without long-term complications. However, early diagnosis and intervention are crucial.
Conclusion:
As we near the conclusion of this comprehensive guide, let’s summarize the key takeaways regarding sports hernia: Recap the essential information about sports hernia, including its definition and symptoms. Highlight the significance of early diagnosis and seeking professional medical advice. Emphasize the importance of preventive measures, core strengthening, and balanced training.




