Who is an Endocrinologist?
Endocrinologists play a crucial role in maintaining hormonal balance and overall well-being. In this article, we will explore the field of endocrinology, the importance of hormonal health, and the role of endocrinologists in diagnosing and treating hormonal disorders.
Endocrinology
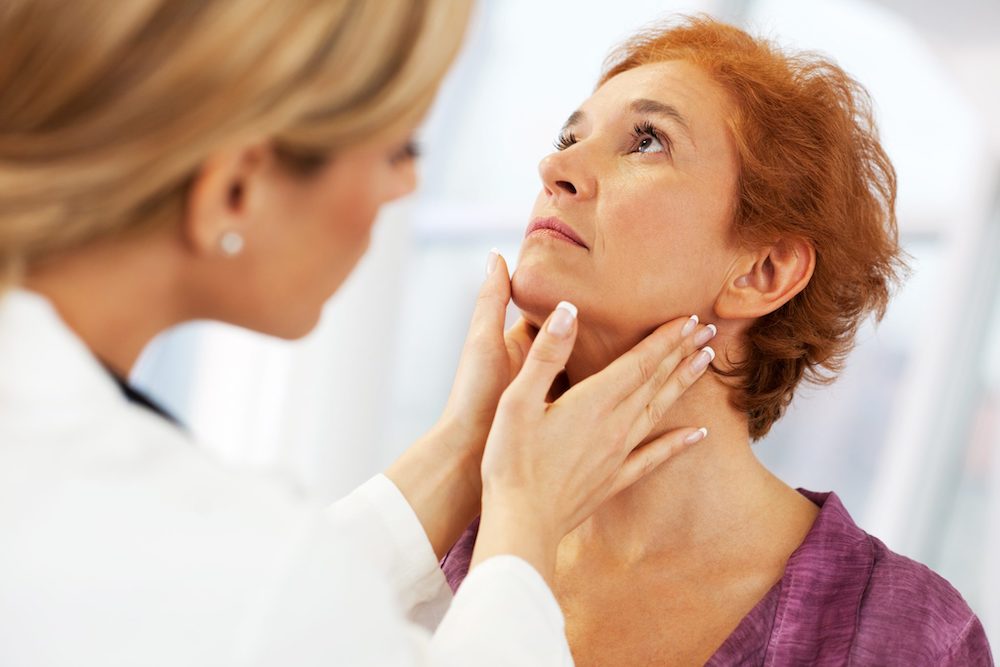
The endocrine system, consisting of glands and hormones, regulates various bodily functions. Hormones act as chemical messengers, controlling metabolism, growth, reproduction, and more. Endocrinologists specialize in diagnosing and treating hormonal disorders, ensuring optimal health through hormonal balance.
Importance of Hormonal Balance
Hormonal balance is vital for overall well-being. When hormones are imbalanced, it can lead to various health issues such as diabetes, thyroid disorders, hormonal imbalances, growth and development issues, osteoporosis, and more. Endocrinologists help restore and maintain hormonal balance, improving quality of life.
Becoming an Endocrinologist
Becoming an endocrinologist requires extensive education and training. After completing medical school, aspiring endocrinologists undergo residency programs focused on endocrinology. This specialized training equips them with the knowledge and expertise needed to diagnose and treat hormonal disorders.
Education and Training
Endocrinologists begin their journey by obtaining a medical degree. They then pursue a residency program in internal medicine or pediatrics, followed by a fellowship in endocrinology. This rigorous training ensures they have a deep understanding of the endocrine system and its complexities.
Dedication and Commitment
Endocrinologists are dedicated professionals committed to their field. They continuously update their knowledge to stay at the forefront of advancements in endocrinology. Their expertise allows them to provide comprehensive care and personalized treatment plans for patients with hormonal disorders.
Common Conditions Treated by Endocrinologists
Endocrinologists diagnose and treat a wide range of hormonal disorders. Some of the common conditions they address include:
Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic condition characterized by high blood sugar levels. Endocrinologists play a crucial role in managing diabetes, providing personalized treatment plans, and helping patients maintain optimal blood sugar control. They may prescribe medications, recommend lifestyle modifications, and monitor long-term complications associated with diabetes.
Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism, occur when the thyroid gland produces too little or too much thyroid hormone. Endocrinologists diagnose these conditions through blood tests and imaging studies. They then develop treatment plans to restore thyroid hormone levels, alleviating symptoms and improving overall well-being.
Hormonal Imbalances
Hormonal imbalances can affect various aspects of health, including reproductive health, metabolism, and mood. Conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and adrenal disorders fall under this category. Endocrinologists use a combination of diagnostic tests and medical interventions to restore hormonal balance and manage symptoms.
Growth and Development Issues
Endocrinologists also specialize in addressing growth and development issues in both children and adults. They evaluate factors such as short stature, delayed puberty, and hormonal deficiencies to develop appropriate treatment plans. By optimizing hormonal levels, endocrinologists support healthy growth and development.
Osteoporosis and Bone Health
Endocrinologists are involved in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of osteoporosis, a condition characterized by weak and brittle bones. They assess bone density, evaluate hormonal factors contributing to bone health, and prescribe medications or recommend lifestyle modifications to prevent fractures and improve bone strength.
Other Conditions
In addition to the above, endocrinologists also address conditions such as obesity, infertility, menopause, and more. They provide personalized care and tailor treatment plans to address the specific needs of each patient.
Diagnostic Techniques and Treatment Approaches
Endocrinologists utilize various diagnostic techniques to assess hormonal imbalances and determine the most appropriate treatment approaches. Some common diagnostic tests include:
Blood Tests
Endocrinologists analyze blood samples to measure hormone levels and identify any abnormalities. These tests provide valuable insights into the functioning of the endocrine system and help guide treatment decisions.
Imaging Studies
Imaging techniques such as ultrasound, MRI, or CT scans may be used to visualize the endocrine glands and detect any structural abnormalities or tumors that may be affecting hormone production.
Hormone Stimulation or Suppression Tests
In some cases, endocrinologists may administer substances to stimulate or suppress the production of specific hormones to assess the functioning of the endocrine system and identify any underlying issues.
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT)
Hormone replacement therapy involves the use of medication to supplement or replace deficient hormones in the body. This approach is commonly used in conditions such as menopause or hypothyroidism to alleviate symptoms and restore hormonal balance.
Lifestyle Modifications
Endocrinologists recognize the importance of lifestyle factors in managing hormonal disorders. They may recommend dietary changes, exercise regimens, stress management techniques, and other lifestyle modifications to support hormonal balance and overall well-being.
Surgical Interventions
In certain cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove tumors or correct structural abnormalities affecting hormone production or secretion. Endocrinologists work closely with surgeons to plan and execute these procedures when required.
Collaborative Approach
Endocrinologists often collaborate with other healthcare professionals, such as nutritionists, psychologists, and primary care physicians, to provide comprehensive care to their patients. This multidisciplinary approach ensures that all aspects of a patient’s health are considered and addressed.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are answers to some commonly asked questions about endocrinologists and their role in managing hormonal disorders:
What symptoms indicate the need to see an endocrinologist?
Common symptoms that may indicate the need to see an endocrinologist include unexplained weight changes, fatigue, changes in appetite, irregular menstrual cycles, excessive thirst or urination, and mood swings.
How often should one visit an endocrinologist?
The frequency of visits to an endocrinologist depends on the specific condition being treated. Initially, more frequent visits may be required for diagnosis and treatment planning, followed by regular check-ups to monitor progress and adjust treatment as needed.
Can hormonal imbalances be managed without medication?
In some cases, lifestyle modifications alone may be sufficient to manage mild hormonal imbalances. However, for more significant imbalances, medication or hormone replacement therapy may be necessary to restore hormonal balance effectively.
Are there any natural remedies for hormonal disorders?
While some natural remedies may provide relief for certain symptoms, it is essential to consult with an endocrinologist before trying any alternative treatments. They can guide the safety and efficacy of natural remedies in managing specific hormonal disorders.
What should I expect during my first visit to an endocrinologist?
During the first visit, the endocrinologist will review your medical history, conduct a physical examination, and order any necessary diagnostic tests. They will then discuss the findings with you, provide a diagnosis, and develop a personalized treatment plan.
How long does it take to see improvements with hormonal treatments?
The time it takes to see improvements with hormonal treatments varies depending on the specific condition being treated and individual factors. Some individuals may experience improvements within a few weeks, while others may require several months of treatment to achieve desired outcomes.
Are there any risks or side effects associated with hormone replacement therapy?
Like any medical treatment, hormone replacement therapy may carry some risks and side effects. The specific risks depend on the type of hormone being replaced and individual factors. Endocrinologists carefully monitor patients undergoing hormone replacement therapy to minimize potential risks and ensure optimal outcomes.
Can endocrinologists help with weight loss?
Endocrinologists can play a role in managing weight-related issues, especially when they are linked to hormonal imbalances. By addressing the underlying hormonal factors contributing to weight gain or difficulty losing wweight anddeveloping personalized treatment plans, endocrinologists can help individuals achieve their weight loss goals more effectively.
What is the difference between an endocrinologist and a gynecologist?
An endocrinologist specializes in diagnosing and treating hormonal disorders that affect various systems in the body. They focus on the endocrine system as a whole. On the other hand, a gynecologist primarily deals with the reproductive system in women, including issues related to menstruation, fertility, and pregnancy. While there may be some overlap in certain conditions, the scope of practice for each specialty is distinct.
Can endocrinologists treat children with hormonal disorders?
Yes, endocrinologists are trained to diagnose and treat hormonal disorders in individuals of all ages, including children. They have specialized knowledge in pediatric endocrinology and can address conditions such as growth and development issues, puberty disorders, and hormone imbalances in pediatric patients.
Conclusion
Endocrinologists play a vital role in maintaining hormonal balance and overall well-being. They are highly trained specialists who diagnose and treat a wide range of hormonal disorders, ensuring optimal health for their patients. By understanding the importance of hormonal balance and seeking professional help when needed, individuals can take control of their hormonal health and improve their quality of life.




