Results of a large study Recurrent published
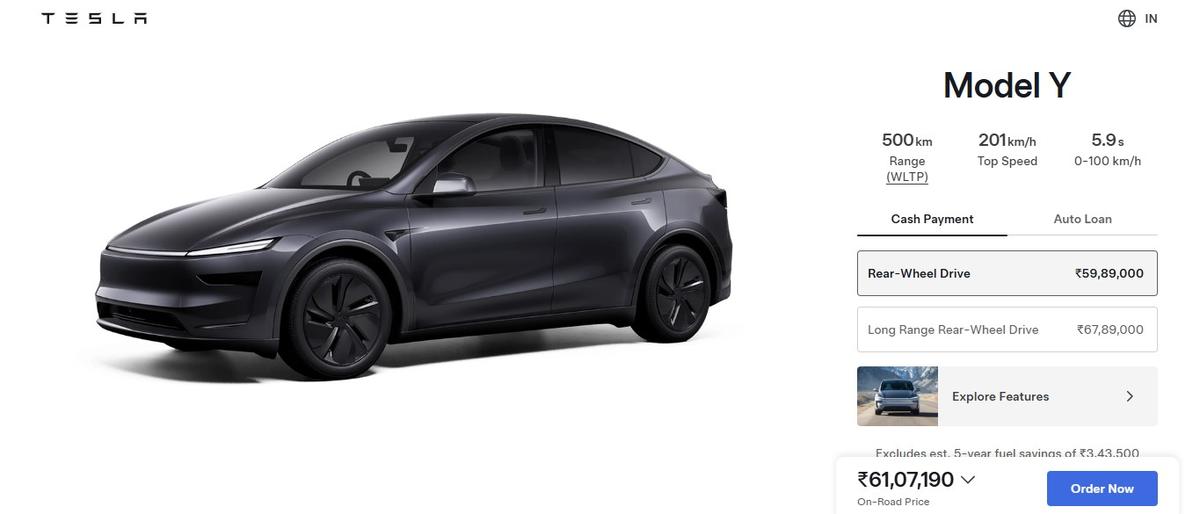
During the 2022-2023 winter season, startup Recurrent collected data on the battery health and range of 10,000 electric vehicles to analyze how freezing temperatures affected their range. Analyzing 18 electric vehicle models in the United States, the researchers found that the average observed winter range (taking into account real-world variables such as climate, terrain and driving habits) was 70.3 percent of their normal range.
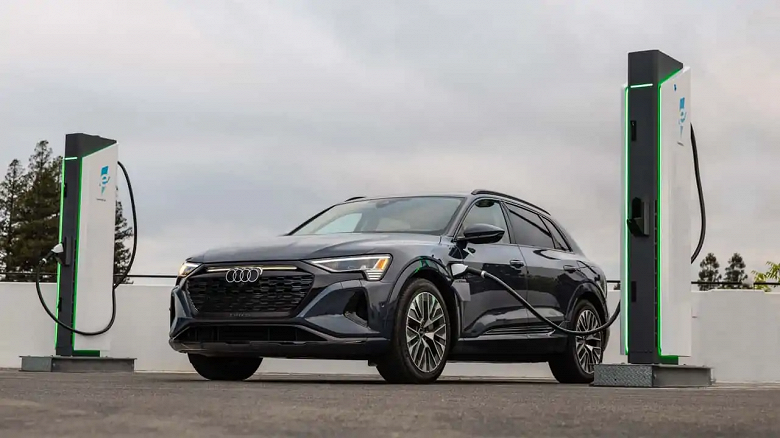

Among the EVs analyzed, the 2021-2022 Audi E-Tron, renamed the Q8 E-Tron starting in 2023, had the smallest range drop at 0°C. Its winter range was only 16% lower than normal. The E-Tron was one of the first electric vehicles to be equipped with a heat pump, which can capture up to 3 kW of electricity by converting waste heat from the engine.
The 2019 Nissan Leaf also saw a relatively small decrease in range. He lost 23% of his range. Note that older Leaf models were more susceptible to varying temperatures due to passive temperature control compared to newer models that can be used with battery warmers. Notably, some Alaska drivers are extremely happy with their Leafs, according to Recurrent.
Tesla, Audi and Nissan lose less range in winter than others
Finally, Tesla’s thermal management looks quite impressive. Model 3, Model Y and Model X lost their range by an average of 24% in the winter. In 2021, the brand introduced its patented heat pump, which seems to have included several innovations to improve the efficiency of the heat pump. Features such as battery preconditioning also help reduce range loss in winter.
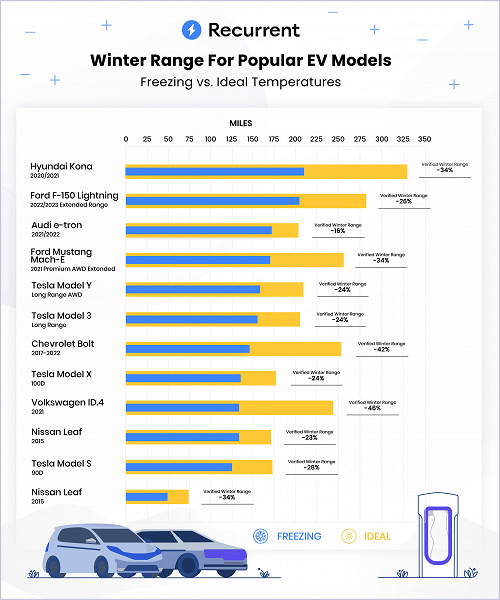
It is worth noting that in colder regions the range may be even less.